An in-person visit to a doctor can be intimidating. Besides, healthcare workers don’t have the capacity to attend to everyone. Multiple studies predict that the shortage of physicians will only increase, reaching up to 122,000 by 2032. As a result, many people may be deprived of quality care.
Would you like your business to avoid the healthcare collapse?
Invest in telemedicine app development. mHealth and Telehealth apps are a trending solution that connects patients and healthcare specialists remotely. For a reasonable fee, users can consult with doctors to solve their health problems and reduce the load on the healthcare system. Some telemedicine solutions even support insurance coverage.
In addition to benefiting end-users, telemedicine development is also a profitable business niche. The telemedicine market is expected to grow at a 16.4% compound annual growth rate by 2032. By entering it now, you join the rapidly evolving niche and increase your chances of taking the lead.
Learn how to develop a telemedicine app, telemedicine app development cost, and other useful tips in our telemedicine app development guide.
What is Telehealth Software
Telemedicine emerged when the first radiology images were transmitted via telephone in the 1940s. After that, many clinicians began to exchange patient data remotely, which has evolved into the telemedicine we know now.
Today, telemedicine is about different kinds of applications, web services, and devices that enable patients or caregivers to benefit from the help of qualified physicians, regardless of their location. The communication happens through phone, video calls, or messaging. Telemedicine app development is used for many types of remote healthcare services, such as telenutrition, telepharmacy, telerehabilitation, telepsychiatry, and others.
Telemedicine Apps Market Overview
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly accelerated the growth of the telemedicine market. It has shown the weaknesses of the global healthcare systems that failed to manage millions of patients remotely. That was a powerful and unexpected punch to everyone, including software providers. Telemedicine software development services have been nudged into seeking solutions that can optimize the work of physicians and enable them to provide remote care.
Now, the increasing rates of chronic diseases are another strong factor that speeds up the growth of telemedicine app development solutions, making providers look for ways to minimize in-person involvement. The estimated global cost of chronic diseases will reach $47 trillion by 2030. Telehealth mobile app development is one of the key ways to optimize expenses and cover the demand, at least partially.
Global Market Insights states the most popular telemedicine market segments are teleconsulting and telemonitoring. This proves that most users look for basic services as an easy way to solve their health problems. Find more insights about the telemedicine industry and telehealth trends in our recent blog posts.
Types of Telemedicine Applications
Each type of telemedicine app development solution is reshaping healthcare, offering flexibility and accessibility in different specialties. If you wonder how to build a telemedicine platform, analyzing available app types is one of the essential steps. Review the main categories of telemedicine applications in our telemedicine app development guide below.
| Real-Time (Synchronous) Telemedicine | It’s just like a regular doctor’s appointment but conducted via video calls. It’s perfect for regular check-ups, catching up after a treatment, or even therapy sessions. Users can visit medical professionals without leaving home simply by using video conferencing apps. |
| Store-and-Forward (Asynchronous) Telemedicine | Unlike real-time telehealth apps, this type doesn’t require the simultaneous presence of doctor and patient. Doctors can send data, such as skin images, heart readings, or test results, to another specialist who will review it later on (asynchronously). The system securely stores all the details. |
| Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) | RPM enables doctors to remotely monitor patients without requiring them to visit a hospital or clinic. Using wearable devices, patients can track vital health indicators such as heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels wherever they are. This is especially useful for caring for people with chronic health problems, those recovering from surgery, and older adults who require regular monitoring. |
| mHealth (Mobile Health) | mHealth apps turn smartphones or tablets into personal health assistants. For example, apps like MyChart allow you to see test results, schedule doctor’s appointments, and even refill prescriptions. They’re also great for learning more about your health, reminding you to take medications, and helping manage chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease. |
| Telepsychiatry | Telepsychiatry covers everything, from online therapy sessions to psychiatric evaluations, and even helps manage meds. For instance, platforms like Talkspace or BetterHelp offer video or text-based therapy sessions, connecting users with mental health professionals from anywhere. |
| Teledermatology | This application enables dermatologists to remotely assess skin issues based on high-quality photos. It helps diagnose skin problems, share advice, and prescribe treatments. For example, apps like First Derm or DermatologistOnCall allow users to upload pictures, and then a dermatologist reviews them and provides feedback and recommendations. |
| Teleradiology | This type of telemedicine app allows users to share radiological images like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with radiologists. Clinicians check these images and give their expert opinions, no matter where they are. A great example is RadNet, which provides a platform for radiologists to access and interpret medical images remotely. |
| Telepathology | Similar to teleradiology, telepathology apps support sharing images and slides for diagnostics, consultations, and even educational purposes. It enables more efficient collaboration among pathologists, regardless of their physical location, enhancing the speed and accuracy of diagnoses. |
| Teleophthalmology | These apps offer eye care services, including exams, diagnostics, and remote monitoring. A good example is EyePACS, which provides a platform for remote diabetic retinopathy screening and the treatment of other eye conditions. Users can get their eyes checked and monitored by specialists through digital images. |
| Telecardiology | This type of telehealth software utilizes the electronic transmission of cardiovascular images and health data for diagnosing and managing patients with heart conditions. A great example is the AliveCor KardiaMobile device. It’s a small, portable device that allows you to perform an electrocardiogram (EKG) from home. You use it to record your heart activity and can send the results electronically to your cardiologist. |
| Teledentistry | Teledentistry apps enable dental care and consultation through digital communication tools, including the assessment, diagnosis, and planning of treatment remotely. A standout example is SmileDirectClub, which offers virtual dental assessments. You can use this platform to have your dental health checked, get a diagnosis, and even plan out treatments without having to visit a dental clinic. |
Learn more about types of telehealth systems by functionality and care modality.
Step-by-step Instructions on How to Develop a Telemedicine App
To create a telemedicine consultation app, you must follow the standard software development lifecycle. Let’s cover the main stages and what matters at each of them below.
Step 1. Run business analysis
Business analysis and identifying a buyer and end-user persona are the first steps to take. Once the target audience (e.g., patients, doctors, or hospitals) and its main needs are clear, it becomes easier to research the market and build a telemedicine platform tailored to a specific niche.
At this point, you will need to turn your idea on how to build a telemedicine platform into something more defined and data-driven. You should gather the following information:
- Target audience and their needs
- Current and potential demand
- Key competitors, their features, monetization models, value proposition, distribution channels, etc.
- Local telemedicine laws and regulations
This information should help you understand what telemedicine app is more likely to attract users and whether you can withstand the competition in the selected niche. It’s also a preparatory step before finalizing requirements.
Step 2. Finalize functional and compliance requirements
Now, it’s time to utilize the gathered information and market analysis to develop a telemedicine app concept. We can help you do it as a telemedicine software development company. Write down potential telemedicine app features and determine which ones you are going to build first. The RICE, Kano Model, and Impact-Effort Matrix are the most common approaches for prioritization.
By ordering functional requirements, you receive a clear roadmap for where to start telemedicine app development and can allocate resources based on the importance of different features. It may turn out, after the analysis, that some features are unnecessary or offer a too low value to invest in them.
Apart from finalizing functional requirements, you must also determine how local regulations impact telemedicine app capabilities, such as data encryption, audit logs, activity monitoring, data retention and deletion policies, and role-based access control. We recommend consulting with a legal expert or cooperating with a software development company that has relevant expertise to know for sure and avoid penalties.
Step 3. Plan telemedicine app development
Identify project scope and plan software development lifecycle based on one of the effective project management approaches like Scrum or Kanban. Agile methodologies work well for complex projects with multiple features that require iterative development.
You must have a clear project schedule with milestones and KPIs to meet deadlines and proceed smoothly. At Empeek, we assign experienced project managers who coordinate the work and make sure the engineering team follows the initial roadmap. If new features or issues arise, you will need to review the sprints and reevaluate the scope of work.
Step 4. Design the app and create a prototype
The next stage in our telemedicine app development guide is a minimum viable product. The design team creates the model of the future telehealth application to showcase its look and functionality. The MVP is a must-have to test the basic version of the app before coding and start marketing the product. At this point, it’s easy to make any changes to the app based on the first user feedback.
Step 5. Develop and test the telemedicine app development solution
The development and testing stage requires much more time and effort than other stages. Developers create the alpha version of the software and share it with QA engineers to begin testing. The duration and scope of telemedicine app development depend on the complexity, technology stack, and functionality of your future app.
Using the combination of testing approaches, the QA team checks the application for bugs and other flaws. If any problem is detected (which usually happens with the alpha version), the software engineers can fix it before the final release.
To speed up this stage, you can integrate various APIs with your app. They will provide you with ready-made functionality, so you won’t need to code everything from scratch.
At this point, you will also need to certify your app based on the relevant industry standards. The 21st section of the Code of Federal Regulations relates to apps with e-prescriptions; IEC 82304-1:2016 is used for apps integrated with devices or medical sensors.
Step 6. Release the software and ensure maintenance
The development team releases the application, making it available to end-users. Several tech specialists continue to work on the project to support the application, troubleshoot issues, fix detected bugs, and implement new features as necessary. Software maintenance is an ongoing telemedicine app development stage.
If you need assistance going through these stages, consider outsourcing the project to a third-party vendor. Empeek can provide you with end-to-end software development, covering each step from market research to app release and maintenance.
In-House vs. Outsourcing Telehealth Development Services
Companies investing in custom telemedicine app solutions must choose between two options: developing software in-house or hiring a third-party vendor. If you have never managed healthcare software development and do not have an in-house engineering department, hiring a telemedicine software development company may be a better choice. For startups or tech vendors specializing in engineering, external consulting help may be enough for successful telemedicine app development with their own resources. Let’s briefly review what each option includes.
In-House Telemedicine App Development
This option may be suitable if telemedicine app development is not your first engineering project and you know how to do it. You may already have an in-house engineering team or sufficient investment to gather one. However, despite sounding simple, staffing healthcare engineers is costly and time-consuming. You may spend months finding the right candidates, and the rates will be high. In-house telemedicine app development gives you full control over the process, and the engineers are better aligned with corporate goals, but the resources it takes are considerable.
Best for:
Companies with a long-term roadmap and the need to build a core product.
Outsourcing Telehealth Development Services
Outsourcing enables you to achieve significantly lower telemedicine app development costs compared to in-house development. You are also more flexible and can scale your remote team size up or down as needed. The key drawbacks of remote software development are that you have less control over the SDLC and can face cultural barriers. Yet, these issues are manageable with project tracking software and regular reporting.
Telemedicine app development outsourcing allows you to build a dedicated remote team consisting of engineers, QAs, designers, a project manager, and other roles required to build an application end-to-end, or you can hire specific tech professionals remotely as your current team extension. The team extension model enables you to grow your in-house engineering department more quickly and optimize expenses.
Best for:
Companies that value speed of development, have a limited budget, or need someone with more expertise.
Critical Factors for Successful Telemedicine App Operation
The successful implementation and sustainable operation of telemedicine applications depend on several critical factors, such as buy-in from healthcare providers, security, and interoperability. These elements support the secure and efficient delivery of healthcare services. Let’s delve into these key factors below.
Healthcare Provider Buy-in
Buy-in from healthcare providers is fundamental to the success of any custom telemedicine app. Medical facilities must be ready to adopt the technology and have a thorough understanding and belief in its benefits. Training medical professionals on how to use telemedicine platforms is essential. This training should extend beyond basic operational knowledge, encompassing an understanding of how telemedicine software can enhance patient care, improve workflow efficiency, and integrate seamlessly into existing healthcare practices. According to a recent survey, 83% of physicians found that telemedicine enhances the continuity of care for chronically ill patients. Sixty-five percent believe telemedicine apps improve communication with patients. When healthcare providers are fully on board, they become advocates for the technology, which is crucial for broader acceptance and use.
Compliant Software & Strict Security
Telemedicine software must adhere to data privacy and healthcare compliance needs, such as the HIPAA and HITECH Act in the United States and GDPR in the EU. Safeguarding patient data involves robust encryption methods, secure data transmission, and stringent data storage practices. Trust in telemedicine systems is heavily reliant on their ability to protect sensitive patient records; any breach can significantly undermine the credibility of the platform.
Interoperability Across Devices
Due to the variety of digital devices and healthcare systems, the ability of telemedicine solutions to work across different platforms and devices is crucial. This means supporting telemedicine applications on both desktop computers and mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. Telemedicine apps must also seamlessly integrate with existing systems, including pharmacies, billing platforms, labs, scheduling software, etc. Besides, the medical software must comply with key interoperability standards, such as HL7 and FHIR, for structured data exchange. The goal is to make telemedicine as inclusive and user-friendly as possible, accommodating the diverse tech ecosystems of patients and healthcare providers.
Tips to Make a Telemedicine Platform HIPAA-Compliant
Compliance with HIPAA requires ongoing effort and monitoring. By following these steps, healthcare providers can create a telemedicine platform that prioritizes patient privacy and data security, aligning with HIPAA requirements.
- Implement technical safeguards such as data encryption in transit and at rest, strong access controls, and secure transmission protocols. Ensure that physical safeguards are in place, such as secure data centers and restricted access to equipment.
- Establish administrative safeguards through privacy policies, data breach response plans, workforce training, and regular audits.
- Obtain Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) with third-party vendors with patient data access.
- Secure communication channels used for telemedicine, employ secure storage and backup measures and regularly train staff on HIPAA compliance.
- Conduct audits and assessments to monitor security controls and establish incident response and reporting protocols.
Note that consulting legal and security experts with healthcare and HIPAA expertise is crucial to ensure adherence to regulations. Compliance can be tricky, so it’s better to invest in professional assistance than to face considerable fines after launching a telemedicine app.
Telemedicine App Development Cost: What to Factor In
Most companies planning how to develop a telemedicine app want to know its cost from the start. The truth is that no one can provide you with an estimate until the requirements are clear.
Generally, the budget for developing a telemedicine mobile app in the US ranges from $80,000 to $ 150,000 or more. The final amount will depend on the complexity of an app and the number of platforms you need to cover. Native apps are typically more expensive, as they require separate versions for iOS and Android. Enterprise-level systems also take more telemedicine app development costs and time to develop.
In addition to telemedicine app development complexity, other price-formating factors include:
- Migration of legacy data and integration with other systems
- Complexity of the regulatory landscape
- Seniority of software developers required to build the app
- In-house development or outsourcing of software engineering services
- Location of the engineering team
The best way to learn the cost of custom telehealth solutions is to consult with professional software development services. You can also read our guide on the cost of implementing a telehealth system for more insights.
Monetization Approaches for Telemedicine Apps
The primary goal of anyone investing in telemedicine app development is making money through paid consultations, subscription charges, and other approaches listed below. The monetization model largely depends on the app type and whether you develop a telemedicine app as a healthcare provider or a tech vendor planning to sell it. Without proper monetization, you won’t be able to achieve a decent ROI and earn money to further improve the app.
- Subscription-based model. Patients or providers pay a recurring monthly/annual fee to access the service. This approach is most effective for platforms focused on chronic care, mental health, and wellness.
- Pay-per-consultation. Users pay for a specific consultation with a doctor booked through an online platform. The revenue from such monetization depends on the volume of patients. The model is a common choice for general practice and specialist telemedicine services.
- Freemium model. Freemium means that basic features are free, but users must pay for more advanced functionality like wellness coaching. This model is an optimal option for telemedicine app development solutions for health tracking and other self-care apps.
- Affiliate revenue. The app promotes partner services, allowing you to earn a commission on sales or referrals (e.g., insurance partnerships). It works well for niche health segments like diabetes care management, where you can recommend relevant products.
- In-app advertising. The telemedicine app displays third-party ads, generating profit from impressions. This model can work well for apps with high user traffic and focus on general health management services.
- White-labeling. With this monetization approach, you provide the app to third parties under their branding. White-labeling is a preferred model by B2B-focused startups or provider networks.
There is no need to focus on a single approach. Many companies combine multiple monetization models, adapting them to different target audiences to maximize profit. For example, Teladoc generates a significant portion of its revenue from B2B subscriptions while also offering individual plans and chronic health management through Livongo.
Tech Stack for Telemedicine App Development
If you are about to launch telemedicine app development, you need to assemble a team of software engineers, UI/UX designers, testers, business analysts, and a project manager with relevant experience and skills. Below, we highlight the core technologies and tools that are used when building an app for telemedicine.
| Frontend | Web: React.js, Angular, or Vue.jsMobile: React Native, Flutter (cross-platform), Swift (iOS), Kotlin (Android) |
| Backend | Languages: Node.js, Python (Django/Flask), Ruby on Rails, Java (Spring Boot)Frameworks: Express.js (Node.js), Django (Python)APIs: RESTful or GraphQL for client-server communication |
| Database | PostgreSQL, MySQL (for structured data and transactions)NoSQL: MongoDB, Firebase Firestore (for unstructured or semi-structured data) |
| Cloud and infrastructure | Cloud Providers: AWS, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Microsoft AzureContainers & Orchestration: Docker, Kubernetes |
| Integrations | EHR/EMR: Redox, Health Gorilla, Epic, Cerner APIsPayment Gateways: Stripe, PayPal, BraintreeInsurance & Billing: Availity, PokitDok Notifications: Firebase Cloud Messaging, Twilio SMS, OneSignal |
If you are still unsure about which tech stack is best for your telemedicine app development project, consider using our product discovery services. We can analyze your software concept and help you finalize the requirements, including the suitable technologies.
Cases of Telemedicine App Development and Implementation
Telemedicine platform implementation can solve various patient experience issues, providing patients with easy access to healthcare services. Read about the projects completed by our team to discover how telehealth technologies facilitate medical practice optimization, provide better care, improve patient safety, and bring other benefits.
Remote Monitoring With a Mobile Cardiac Telemetry System
In this project, we have developed a mobile cardiac telemetry system consisting of an ECG patch and a mobile app that monitors the cardiac health indicators of thousands of patients in real time. Our team has designed a cloud-based solution with web and mobile applications, enabling real-time data processing, analysis, and transmission. The system tracks various cardiac health parameters, including ECG, heart rate, SpO2, temperature, and activity level. The project also involved consultation with FDA experts to ensure compliance with regulations.
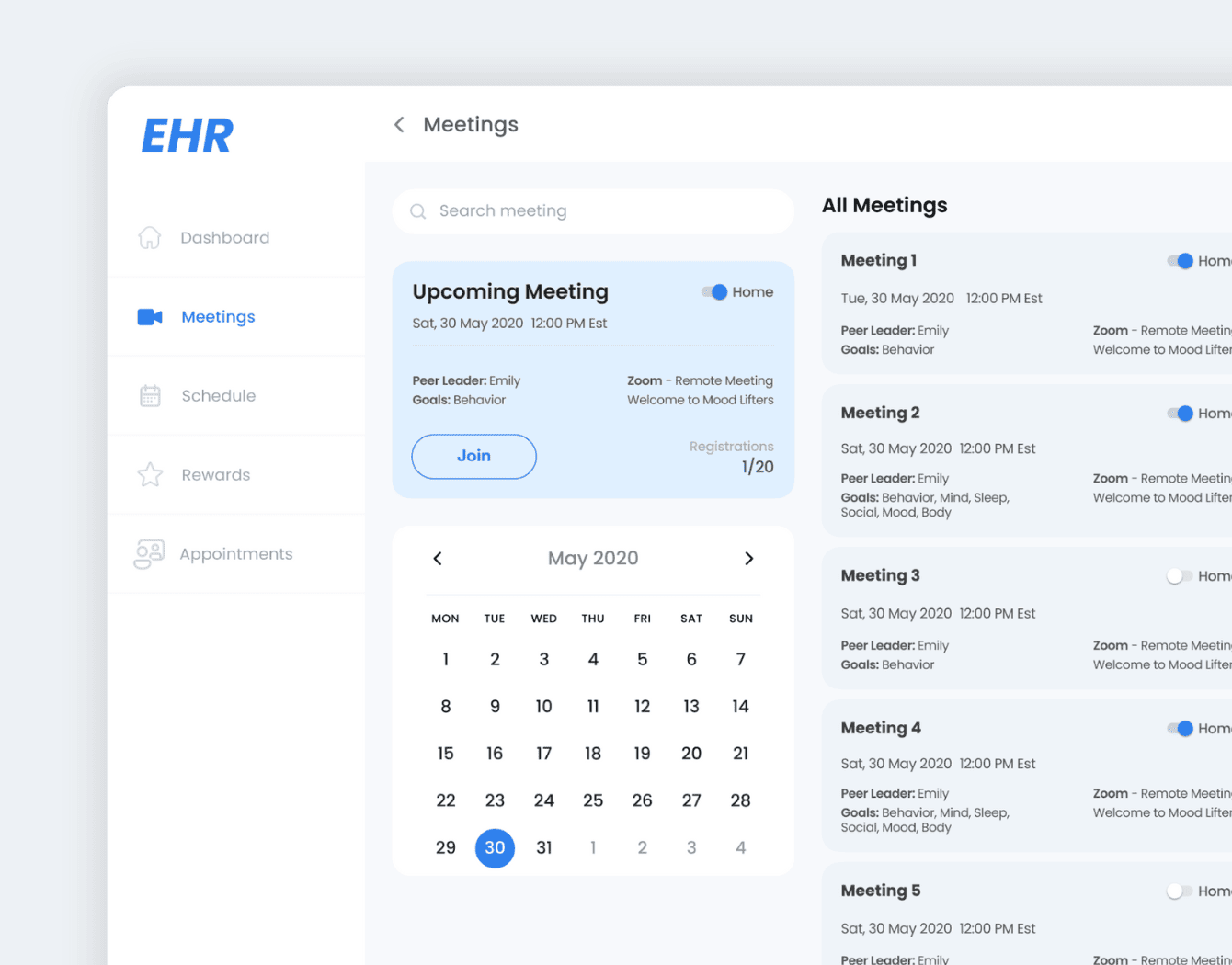
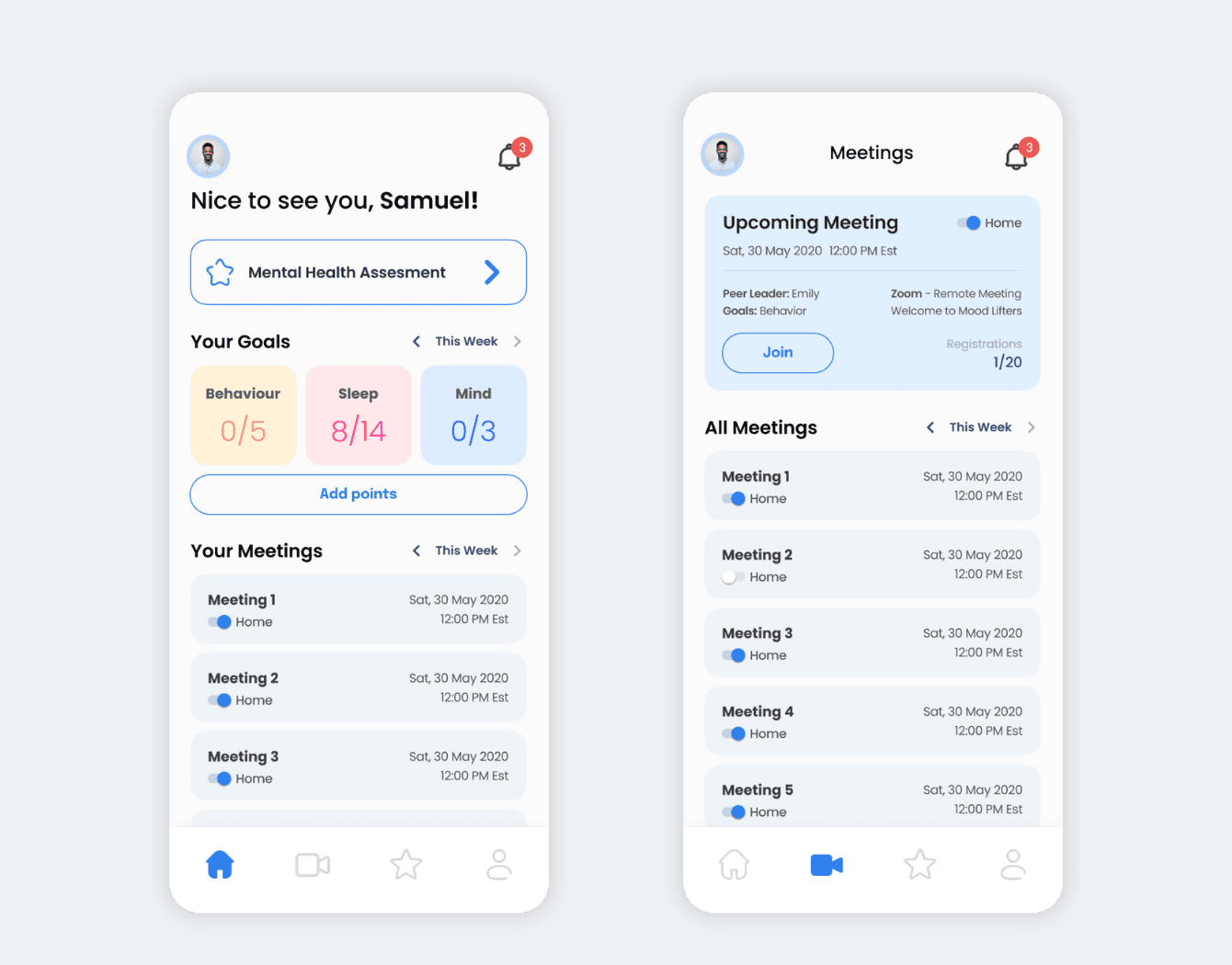
Telehealth and EHR Platform for Behavioral Health
Empeek built a HIPAA-compliant EHR system for behavioral health, along with iOS and Android mobile apps. The system helps patients reduce stress and anxiety by completing specially created surveys, setting up appointments with doctors, tracking weekly achievements, and receiving rewards. The solution includes a sophisticated questionnaire system, patient management, extended reporting, and gamification elements.
Final Thoughts
Telehealth solutions are easy to monetize and highly demanded by healthcare providers and patients. On top of that, they promote wellness and help many people take better care of their health. Therefore, by establishing a telemedicine business, you not only become a part of the rapidly evolving industry but also contribute to healthcare accessibility.
Although to set up a telemedicine business, you need considerable investment, healthcare is among the most promising fields to invest in right now. Empeek’s reliable team of developers can help you join it. Contact us to discuss the idea of your telemedicine project and find the best way to realize it with our telemedicine software development services.








