Telemedicine is super handy when you need a doctor but can’t make it to the clinic. It’s a big help for doctors, too, since they can manage more patients without getting swamped.
In 2024, the number of online doctor consultation users reached 116 million worldwide and is expected to increase to 13.7 million users by 2028. Now, apps with standard features such as appointment scheduling, video consultations, and secure messaging have become a fundamental necessity. Patients expect providers to offer these features as well as innovative add-ons like AI-powered diagnostics and integration with wearables.
If you’re wondering what telemedicine app features to include in your solutions, this article can guide you through the core features. These are essentials to make your healthcare services competitive.
What Matters in Modern Telehealth Apps
The features of a telemedicine app matter, but most people choose one or another app because of the overall experience it offers. Recent research by Deloitte showed that people value convenience as the key benefit of virtual visits. 64% liked that virtual healthcare platforms provided better appointment times, 44% valued the saved time, and 37% appreciated the shorter wait to get an appointment.
The numbers above demonstrate that patients want telehealth technologies to simplify their lives and offer advantages in-person care doesn’t provide. Here are some other preferences backed by research and usage trends:
- Quality of care is still critical. Health is no joke, and telehealth technology users want to be sure that the services they receive online are reliable. This means you must provide close patient monitoring with telemedicine features and communicate to users how the app ensures quality care. Fortunately, in many domains, like chronic illness management, the quality of online services is at the same level as in-hospital care. A multi-site randomized clinical trial involving 1,250 patients with lung cancer showed equal efficiency of both.
- Personalization matters. Providing healthcare services through mobile devices limits the personal connection between a patient and doctor, yet it also brings more advanced customization many people crave. The spread of AI makes integrating virtual assistants, advanced remote patient monitoring, and personalized treatment plans based on patient history more accessible. Users have unlimited attention from tech assistants while doctors step in when they are really needed.
- Educational content on health. Patients want more control over their health and real-time tips based on their health data. In the 2022 online survey, 80% of patients admitted they would be more satisfied with care if they had patient education. A large share of patients also have follow-up questions. That’s why clear medical instructions and educational content are essential in modern telehealth technologies.
- Secure data processing. Personal health information security is not a new trend or unusual concern. People have always been worried about how telehealth tools process PHI, and it hasn’t changed much for a reason. In 2025, over 135 hacking/IT incidents have been detected, and we are not even mid-year. It should lead you to two conclusions: First, always protect data in telehealth technology and comply with regulations; Second, talk to patients about security and make sure they know that your telemedicine app is safe and how to use it properly.
These trends demonstrate why people may choose telemedicine app development over in-person visits and what they want. Convenience matters most, but proper quality, personalization, security, and relevant information can also make your telemedicine app a market leader.
Read also: 5 Telehealth Technology Trends to Follow
Top 15+ Telemedicine App Features to Implement
To know what features of a telemedicine app to implement, you must analyze your target audience and detect user needs and concerns. People are more likely to use telemedicine for a minor illness and still favor in-person visits for specialties like dermatology, with 68% preferring in-person care. According to Deloitte, the highest shares of patients would choose virtual healthcare platforms to refill a prescription, treat a general illness, have a mental health visit, or for preventative care.
The information on what patients seek and understanding the most repetitive healthcare processes will help you determine what telemedicine features you need for virtual care. Here are the core options to consider.
1. Appointment Scheduling
Appointment scheduling in telemedicine applications is a game-changer for patient convenience. This feature allows patients to book, reschedule, or cancel appointments online, reducing wait times and administrative burdens. It often includes calendar synchronization, reminders, and confirmation notifications, enhancing the overall patient experience. The impact of this feature for healthcare providers is substantial: online appointment scheduling is estimated to reach $1,518.4 million by 2032 from $546.1 million in 2025, demonstrating its increasing importance in healthcare management and access to services.
2. Services and Doctors Catalog
These features of a telemedicine app enable patients to browse through available services and specialists. It often includes detailed profiles of healthcare facilities and providers with their qualifications, specialties, and patient reviews. It provides patients with the information needed to choose the right provider and service, fostering trust and transparency in the healthcare process. For instance, Zocdoc offers a platform where patients can browse a list of doctors and services, complete with detailed profiles, credentials, and patient reviews.
3. Patient Portals
A patient portal is a personal health dashboard to check a patient’s medical records, test results, and summaries of doctor visits in one place. They have secure authorization and consolidate health data from multiple providers to ensure the continuity of care.
It’s one of the essential telemedicine app features that helps patients stay on top of their health and feel more connected to healthcare providers. 46% of US consumers, approximately 119 million patients, are now engaging with healthcare providers through a combination of patient portals, telehealth appointments, apps, and in-person visits.
4. HIPAA-Compliant Video Visits
Real-time video meetings are a standard feature in most telemedicine software examples that offer online consultations. Phone calls and messages are suitable for telemedicine apps, but seeing someone in person creates more trust and facilitates communication. That’s why we recommend implementing video visits as one of the core communication channels in your app. And make sure the functionality for video calls meets HIPAA.
HIPAA-compliant video visits make patient-provider interactions secure and private. The requirements are overall the same as for other means of online communication like messages or emails. A safe platform for virtual consultations ensures patient information is confidential and only authorized people can access video and records. Fortunately, there are numerous HIPAA-compliant platforms to connect with telemedicine software for video communications, including Zoom for Healthcare, Doxy.me, and others.
5. Patient Education
Patients want more information about their health and treatment with learning materials, such as videos, articles, and interactive tools tailored to their needs. When patients receive relevant information, they are more likely to adhere to treatment regimens and see better results, which also means being more satisfied with telehealth app features.
Providers can create an extensive library of educational materials related to dieting, lifestyle habits, or preventative measures in telemedicine apps. Such educational materials have great potential for boosting chronic care management since over 142.66 million US citizens aged 50+ years will have at least one chronic disease by 2050. It’s a win-win: patients feel better about their health, and healthcare professionals see happier, healthier patients.
6. Queue Management
Queue management systems let patients know how long they’ll wait and keep them updated on their appointment status. Knowing exactly where you stand in line is a big stress reliever for patients. Providers, on the other hand, see a real-time list of patients waiting for a meeting and update the patient’s status as it changes.
This feature allows providers to manage patient flow better, cut down wait times, and ensure everyone gets the care they need faster. This is super important in busy clinics where many patients receive care and the load is huge.
7. Dashboard With Patient Data
A comprehensive dashboard with patient data presents a consolidated view of patient information, including health history, recent visits, and ongoing treatments. The dashboard telemedicine function also includes contact information, insurance details, the medical record number, and other demographic data for patient management.
A more advanced dashboard may be connected with analytics tools, helping healthcare professionals track health trends and outcomes over time. It syncs with wearables, such as Apple Watch or heart rate monitors, to display patient data in real-time. Such telemedicine features enable providers to make informed decisions quickly, enhancing the quality of care.
8. EHR Integration
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR) is a basic feature in most telemedicine apps, as access to patient records makes online consultations more effective and data-driven. All patient information from telemedicine visits is added directly to the existing EHR system. Healthcare professionals can view the entire health record of a patient, updated with the latest information. Plus, this feature makes the admin side of things a lot smoother and cuts down on the likelihood of making mistakes when entering data.
Connecting through an API, based on FHIR and SMART on FHIR standards, is the primary method for integrating a virtual healthcare app with an EHR. So, make sure such capabilities are included in a telemedicine app. You can use our EHR integration services to connect all the systems smoothly and make the features of a telemedicine app compliant.
9. Chatbot
Chatbots are among the most common uses of AI in telemedicine. They can facilitate symptom assessment, virtual consultations, pre-consultation data intake, health triage, appointment scheduling, follow-up care, medication management, and health education. Given the growing shortage of medical staff, reaching 85,000 physicians by 2036 in the US only, the fact that chatbots are taking routine communications is good news.
If you consider a chatbot as one of the telemedicine app features, you have many low-code platforms for quick integration (e.g., Dialogflow, ChatGPT API, and Microsoft Bot Framework). You can also build a custom solution but mind ethical and data privacy issues. Chatbots were not initially intended for healthcare and do not necessarily provide the necessary level of PHI privacy. Besides, chatbots are usually trained on historical datasets, which means their responses are not based on the latest clinical information. Hence, a chatbot is a great tool to share basic information and support a patient, but it’s not enough for specialized care.
10. Bilingual Communication
Almost 66 million of the US population speak a language other than English at home, and their English level may not be sufficient for having quality doctor consultations. Bilingual communication in telemedicine applications addresses the need for language inclusivity in healthcare. This feature offers services in multiple languages, ensuring that patients who do not speak English can access care without barriers. It often includes translation services for patient-provider interactions and multilingual support for patient educational materials. This inclusivity is crucial for providing equitable remote medical services to diverse patient populations.
11. API Extensibility
API (Application Programming Interface) extensibility lets apps connect and work with other software and services, such as payment gateways (Stripe, PayPal, Square, etc.), social media platforms (Facebook, Instagram, X), messaging and communication tools, calendar services, etc. This way, healthcare organizations can tweak and improve their telemedicine platforms by adding new features. You won’t need to develop new functionality from scratch. API integration makes connecting third-party apps much easier and speeds up the implementation timeline.
12. Virtual Waiting Rooms
Virtual waiting rooms are an important feature in the telemedicine platform, enhancing the patient experience before virtual consultations. They offer a digital space where patients can wait before their scheduled video visit. This feature often includes informational content, estimated wait times, and instructions for the visit. It helps in managing patient expectations and reducing anxiety associated with virtual consultations.
13. ePrescribing and Referrals
ePrescribing allows healthcare providers to send prescriptions directly to pharmacies electronically, reducing errors and improving patient convenience. This feature also includes medication management, helping providers track patient adherence to medication regimens. Besides, telemedicine apps can support prescription renewal requests, enabling patients to request additional medications and doctors to give the green light to these medications right away.
Referrals are another powerful feature of telemedicine apps, enabling seamless integration with specialist care. The referrals typically involve healthcare providers, such as primary care physicians, using the app to connect their patients with specialist doctors within the same telemedicine network. This process allows for a more coordinated approach to healthcare, ensuring that patients receive comprehensive and continuous care. For example, a general practitioner using a telemedicine app can quickly refer a patient exhibiting cardiac symptoms to a cardiologist within the same network.
14. Multi-Party Video Calls
Multi-party video calls enable the inclusion of multiple participants in a telehealth session, such as family members, caregivers, or multidisciplinary medical teams. This feature is useful for complex cases requiring collaborative care or when family involvement is essential for decision-making. You will need to implement role-based access control for multi-party video calls to separate the functionality for doctors, patients, interpreters, and admins. The multi-party video call feature must enable users to mute/unmute participants, manage the waiting room, send messages in the chat, and share screens.
15. Automated Billing and Insurance Verification
Automated billing and health insurance portability verification systems optimize the financial aspects of telemedicine services. These systems can process payments, verify insurance coverage, pay medical bills, handle billing queries, automate claim submission and payment, assign CPT/ICD codes, and more, all while patients use a telemedicine app. This reduces administrative burdens and enhances the efficiency of the overall telemedicine apps. Besides, patients become better informed about their current insurance status and finances.
Learn more about How To Develop A Hospital Billing System
16. Health Risk Assessments
Health risk assessment tools within a telemedicine platform help identify patients at risk for various health conditions. These assessments typically involve questionnaires and algorithms that analyze a patient’s medical history and responses to identify potential health risks. For example, Empeek designed a platform that has a complex questionnaire system to evaluate the mental health of patients. Moodlifters offers its users a comprehensive way to monitor their health conditions and receive on-time support from a community of peers and doctors.
17. Integration With Wearables
Integration with wearable health devices provides access to real-time health data from fitness trackers, smartwatches, and other health monitoring devices. Suppose someone is wearing a smartwatch that tracks their heart rate and sleep patterns; the telemedicine app can use this data to keep a close watch on their health.
Empeek has developed a real-time cardiac telemetry system that monitors vital heart indicators. The patient has a wearable patch that transmits data to the cloud and is visible on patients’ and doctors’ portals. Once there is a deviation from the norm, the algorithm immediately notifies responsible parties so they can promptly provide help.
Types Of Care Patients Can Get Using Telemedicine App Features
You may further customize telemedicine app features by focusing your application on a narrow medical specialty. An all-in-one solution may be too complicated in terms of usability and technical implementation. That’s why you should consider building an app for a specific type of care.
| Acute Health Conditions | Telehealth can manage acute health conditions, which often require prompt attention but are not life-threatening. These are common ailments, such as infections, minor injuries, the flu, or allergic reactions. Through virtual therapy sessions, healthcare providers can assess symptoms, offer diagnoses, and prescribe medications. For conditions that require physical examination, telehealth can serve as an initial step, guiding patients on whether they need in-person care. |
| Chronic Health Conditions | Managing chronic health conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension is where telehealth makes a difference. Through telehealth platforms, patients get the ongoing care and monitoring they need. They can check in with their doctors frequently, share updates from their home monitoring gadgets, and adjust their treatment. Such support improves the management of their conditions, reduces trips to the doctor’s office, and helps detect problems early. |
| Medical Management | Telehealth enables physicians to oversee patients’ medication regimens, ensure adherence, and adjust prescriptions. It also covers post-operative care, with follow-up consultations, wound monitoring, and recovery guidance. Additionally, telehealth provides a platform for preventive care, offering services like health education, lifestyle counseling, and routine health screenings. |
| Mental Health Services | Teletherapy and telepsychiatry services allow patients to connect with mental health professionals for conditions like depression, anxiety, stress management, and others. It’s a confidential way to get help and support without leaving your home. |
| Specialized Consultations | With telehealth, patients can access specialized medical consultations that may not be available in their region. This includes access to specialists in fields like dermatology, endocrinology, or oncology. Patients can receive expert opinions, second opinions, and specialized care plans, all from the comfort of their homes. |
| Rehabilitation Services | Telehealth apps can support rehabilitation services, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. Through virtual sessions, therapists guide patients through exercises, monitor their progress, and adjust therapy plans. This remote model provides convenience and ensures continuity of care, which is particularly important for patients with mobility issues or those living in remote areas. |
Real Use Cases of Telemedicine App Development
Empeek has completed multiple telemedicine app development projects for mental health, remote patient monitoring, cardiac care, and other uses. Read about real telemedicine software examples to draw inspiration for your project.
EHR system and Patient Portal for Mental Health
A US-based mental health clinic faced challenges because of its fragmented operational system. They used separate software for electronic health records (EHR), appointment bookings, and accounting. This disjointed approach caused administrative inefficiencies and a poor experience for staff and patients.

Empeek joined the project to develop a comprehensive HIPAA-compliant EHR system and patient portal. The solution includes a patient-counselor matching algorithm, automated appointment booking with reminders, and an integrated platform for processing medical claims. The system has significantly reduced no-shows and streamlined insurance and self-pay processes. It also offers features like automatic reminders, a centralized document library, and audio-video conferencing for remote consultations.
The implementation, carried out in stages to minimize disruption, has resulted in a seamless transition to a more efficient and integrated system. This change has improved administrative processes and enhanced the overall quality of patient care.
Moodlifters – Mental Wellness App
Moodlifters is an innovative mental wellness program designed at the University of Michigan to make mental healthcare more accessible and destigmatize it. The program offers practical techniques to help users manage stress and anxiety.
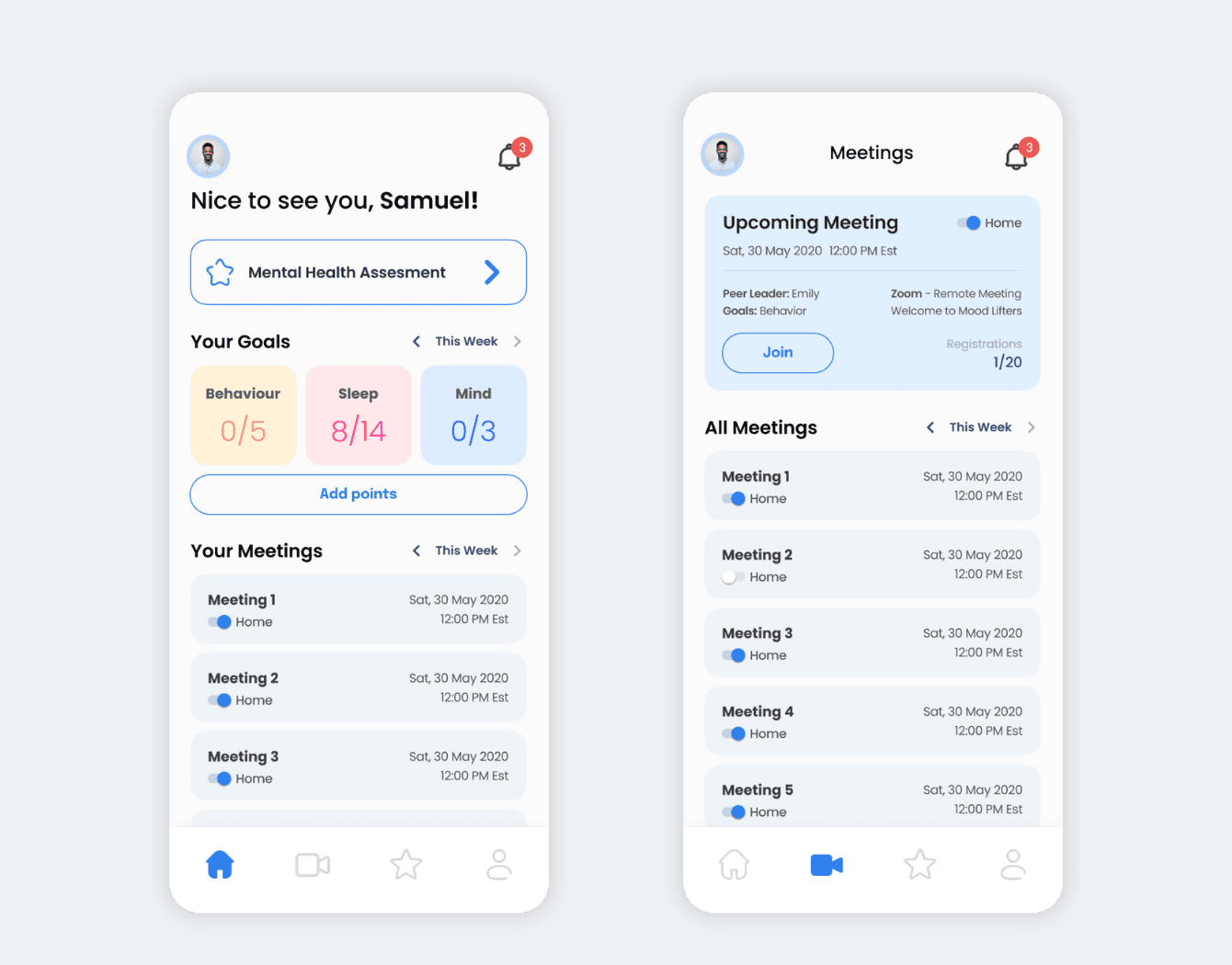
Empeek developed a cross-platform mobile app and web portal for Moodlifters, enhancing its reach and effectiveness. The app provides a reward system, personalized goal setting, and progress tracking. It can be used as a standalone online counseling tool or as a supplement to traditional therapy.
Custom Remote Patient Monitoring Solution
A client partnered with Empeek to develop a custom remote patient monitoring (RPM) solution. The portal uses cellular or Wi-Fi technology to gather health data and transmit it to healthcare providers for evaluation and recommendations.
Software implementation simplifies patient care management decisions, reducing emergency room visits and hospital readmissions. It also helps cut the cost of care for patients and providers.
Learn more about the software we developed from our case studies, or contact us for free consulting.
Takeaways About Telemedicine App Features
This article highlights the importance of a multifaceted approach in creating a telemedicine platform that is patient-centric, efficient, and integrated into the healthcare ecosystem. The telemedicine app features listed here are standard capabilities in telemedicine, but you don’t have to implement all of them. Run a software project discovery and analyze target users to build a combination of features people really need.
As a telemedicine software development company, our expertise in software development can help realize the full potential of your telemedicine platforms.








