The financial sustainability of healthcare organizations depends on the effectiveness of a hospital billing system. Such a platform allows providers to automate all billing processes and keep related documentation in order. You can connect one of the third-party billing systems or develop a custom one fully tailored to your organization’s needs. Yet it’s important to understand that with the global healthcare billing outsourcing market expected to grow to USD 27.32 billion by 2028, the push towards more sophisticated hospital billing management software is stronger than ever.
Read about the various medical billing solutions available and how to build one in our post. You will also learn about the limitations of off-the-shelf solutions and get billing software implementation insights.
What Is Wrong With Off-The-Shelf Hospital Billing Systems?
Pre-built, off-the-shelf solutions are flooding the market. These products offer a quick, ready-to-use approach to the complex billing processes hospitals deal with daily. But is it all as straightforward as it sounds?
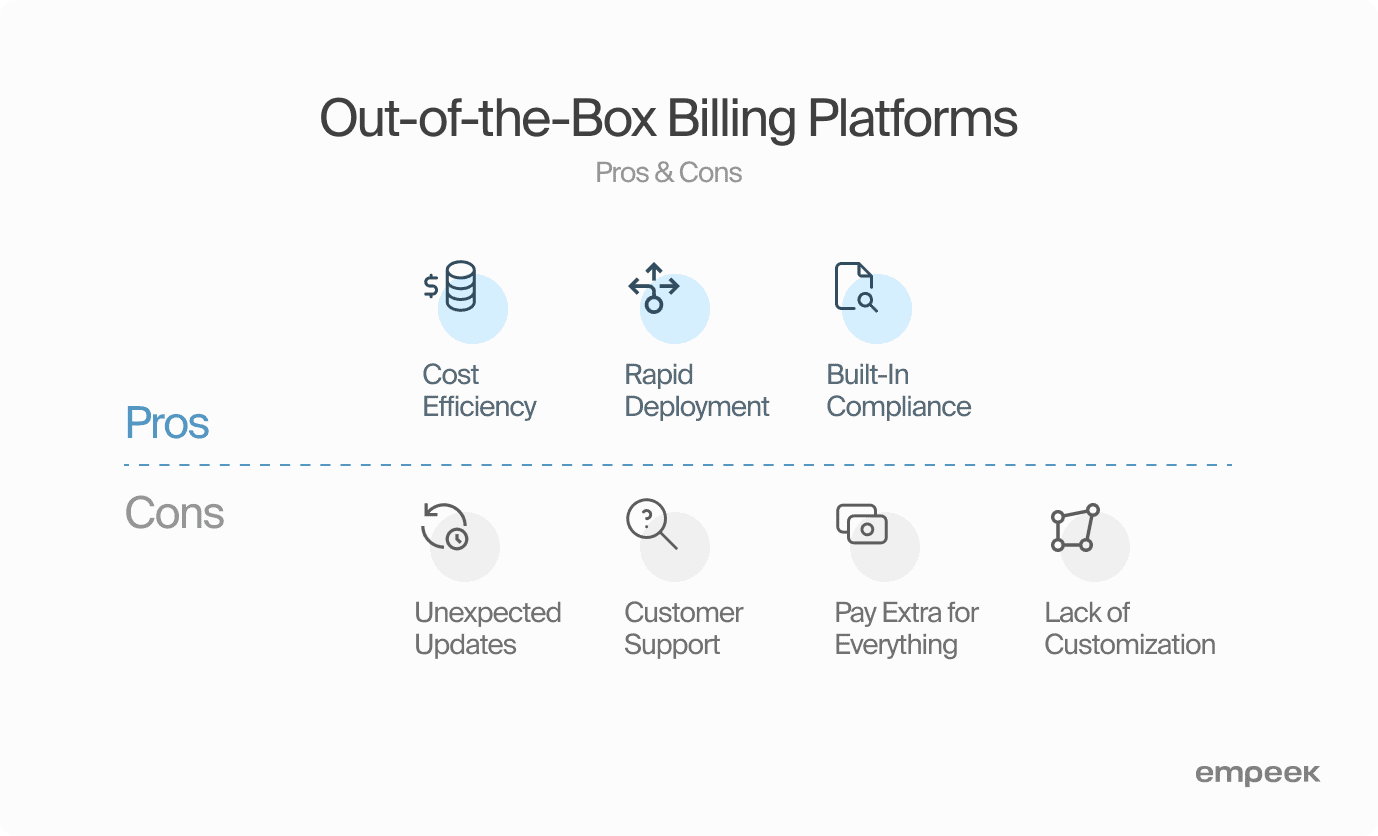
Advantages of Off-The-Shelf Hospital Billing Systems
Quick Deployment
Deployment is typically faster with off-the-shelf systems since they’re ready to go right off the shelf. Hospitals can implement them quickly, bypassing the long development process that custom systems often require. This is especially helpful for hospitals with outdated systems or newly opened facilities.
Compliance
Off-the-shelf billing systems comply with current healthcare standards, including HIPAA, as compliance is a selling point for these products. These systems help hospitals stay on top of the legal standards for safeguarding patient information and handling billing procedures correctly.
Cost-Effective Implementation
Off-the-shelf billing systems are generally less expensive upfront compared to custom-built solutions. Since the development costs are shared across many users, off-the-shelf solutions are more affordable—an appealing option for hospitals operating on a tighter budget.
Disadvantages of Off-The-Shelf Hospital Billing Systems
Unexpected Updates
An unexpected update to the interface or processes in your medical billing system can pose challenges for your staff. Frequent updates and learning new features can slow things down. Teams must constantly retrain, and updates can sometimes mess with previously smooth functions, making them less effective. However, regularly communicated updates and training programs can mitigate disruptions, ensuring a smoother transition to the updated system.
Customer Support
While many medical billing software providers promise 24/7 customer support, the reality may not always align with these assurances. It’s important to carefully evaluate the post-implementation support a provider offers. Instances where major issues linger unresolved and remain “under development” after the implementation phase can be problematic, particularly if the issue is urgent and directly impacts patient health.
Pay Extra for Everything
While off-the-shelf medical billing solutions may appear cost-effective initially, you must consider potential hidden costs, including licensing fees, maintenance costs, and additional features or upgrade charges. As your healthcare business expands, anticipate additional costs for both minor and major add-ons. Although the initial investment may seem lower, a careful examination of the total cost of ownership over time reveals that opting for a seemingly cheaper solution may not necessarily equate to good quality.
Lack of Customization
In an era emphasizing user-centricity, off-the-shelf medical billing systems may fall short in catering to the specific needs of every hospital. The one-size-fits-all approach may not accommodate unique billing processes or specialized services offered by certain healthcare facilities. Choosing a system that isn’t customizable can lead to inefficiencies and may not fully meet your hospital’s unique needs. While a more flexible, customizable option might seem more complex upfront, you must ensure the billing system fits your hospital’s specific workflows and requirements.
3 Types Of Healthcare Billing Systems
When it comes to medical billing systems, understanding how they’re structured is crucial for keeping a hospital’s financial operations running smoothly. Typically, there are three main types: closed systems, open systems, and isolated systems. Let’s take a closer look at what sets these apart.
Closed Medical Billing System
Closed medical billing systems are proprietary platforms designed to work within a specific ecosystem. They are ‘closed’ because they restrict access to data and interoperability with other systems to safeguard data integrity and the workings of the system. Their key features include:
- Integration
Closed systems often integrate well with modules from the same vendor but can have limited compatibility with external systems. - Control
One major advantage is that vendors usually maintain tight control over how the system functions and handles data, which makes them more secure and reliable. - Customization
Customizing or updating closed systems can be challenging, as they require vendor involvement.
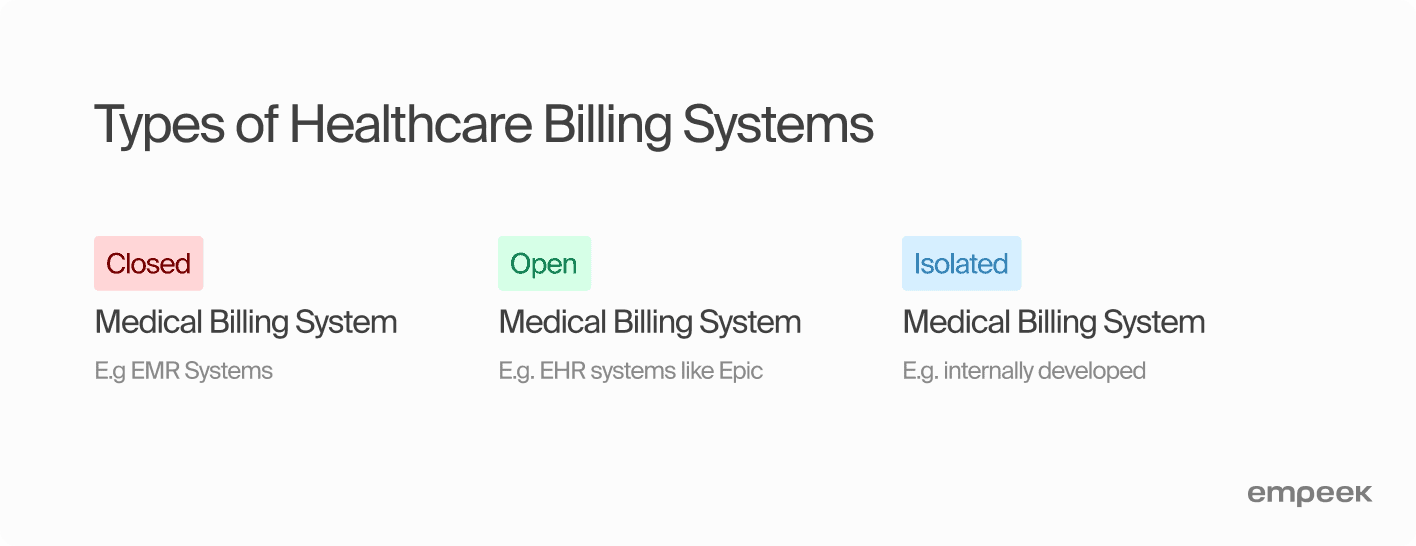
Open Medical Billing System
Open systems are designed with interoperability in mind, using standards and protocols that allow them to interact with other systems easily. They smoothly integrate with other billing functions, offering a well-rounded solution for hospitals. Their main characteristics are the following:
- Integration
These systems are built to communicate with a variety of other systems, regardless of the vendor, facilitating a more connected healthcare IT environment. - Flexibility
Open systems can be more easily customized to meet the specific needs of a hospital. - Collaboration
They encourage collaboration and data exchange between different healthcare stakeholders.
Isolated Medical Billing System
An isolated system, as the name suggests, is a stand-alone solution that is not designed to connect with other systems. It operates independently, and data sharing is not its strong suit. Its main features include:
- Integration
There is little to no native support for integration with other systems. - Security
While they can be more secure due to their isolation, they can also make comprehensive data protection more challenging because of the multiple silos of information. - Data Silos
They inherently create data silos, which can lead to inefficiencies and errors due to multiple data entry points.
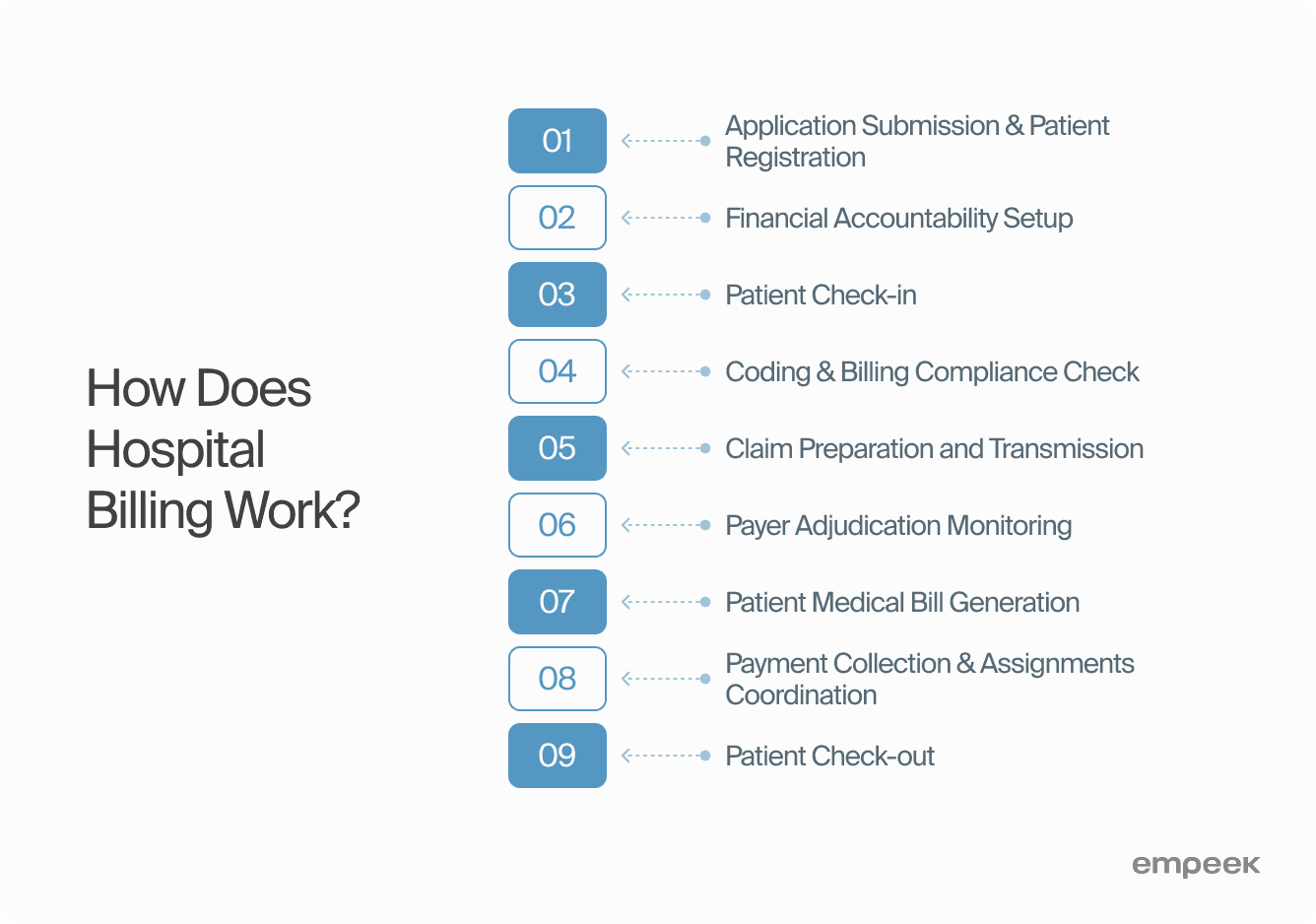
How Does Hospital Billing Work? — Process of Hospital Billing
According to a study published in the National Library of Medicine, an efficient hospital billing process is linked to improved financial performance and patient satisfaction. This highlights the need to fully understand the hospital billing process, uncovering all the different steps and components that form the financial backbone of healthcare.
One important tool in ensuring accuracy in this complex process is the medical billing audit. Regular audits play a key role in spotting billing mistakes, reducing fraud, and staying regulatory compliant. But audits aren’t just about money. They also help ensure billing transparency, which is necessary for maintaining the quality of healthcare services.
Here are the main stages of how the hospital billing system works.
Application Submission & Patient Registration
The journey begins with application forms, the cornerstone of the hospital billing process. Patients provide personal, insurance, and medical history information necessary for pre-registration and accurate billing. These forms are the source data for all subsequent billing activities and must be completed accurately to avoid delays or errors in billing.
Once the application forms are filled out, the patient enters the registration process. This step ensures the recorded information is accurate and updated. It also sets up an electronic medical record that will be used throughout the patient’s time at the hospital, linking every treatment and service to the right person and their insurance.
Financial Accountability Setup
Another key part of hospital billing is establishing financial accountability. This is where you make sure that the patient’s insurance details are correct, clarifying what the patient is responsible for financially and creating a clear framework for billing transparency.
This process helps keep costs under control and inform patients about what they can expect financially. While it can take some effort to get this system running smoothly and train staff, the rewards include better financial stability, fewer billing mistakes, and stronger regulatory compliance.
Patient Check-in
This is a crucial process where individuals provide necessary information like personal info, insurance data, and treatment consent upon arrival for medical services. Proper check-in is essential for accurate billing and efficient administrative processes. It also ensures transparency in financial matters and allows hospitals to provide better, more efficient care.
Coding & Billing Compliance Check
This is a meticulous review process designed to ensure accuracy and adherence to regulatory guidelines in coding and billing practices. Behind the scenes, the medical coder’s responsibility is to review patient records to translate every diagnosis, procedure, and supply used during the visit into standardized codes that are used for billing. The main goal here is to catch any errors, minimize compliance risks, and make sure hospitals get reimbursed properly.
Claim Preparation and Transmission
Prepared claims encapsulate all coded services and costs into a formal bill. A complete claim has the correct medical codes, patient info, and everything else needed. It must be accurate, follow coding rules, and correctly reflect the care provided.
Once ready, the claim is transmitted electronically or through other designated channels for processing and reimbursement to insurance companies. Smooth claim preparation and submission are important for getting paid on time, keeping the hospital financially stable, and ensuring steady revenue cycle flows.
Payer Adjudication Monitoring
The accounts receivable service provider actively tracks and manages the adjudication status, ensuring that claims are processed accurately and efficiently. This step involves making sure claims are accepted, catching any denials or discrepancies, and fixing any issues that come up during the payer’s review process.
By carefully managing the payer’s review process, the accounts receivable service provider helps ensure a smooth flow of revenue. It is during this phase that any issues, such as denials or requests for additional information, are handled.
Patient Medical Bill Generation
Once insurance adjudication is complete, the hospital creates and sends out patient bills or statements for any remaining balances. Using the right coding standards and fee schedules, the hospital creates a detailed bill that clearly lists all the services provided and related costs. The bill includes patient details, insurance information, and deductibles or copayments.
Following thorough verification and accuracy checks, the finalized bill is then delivered to the patient, insurance company, or other responsible parties. This step is key to making sure patients understand their financial obligations and keeping them informed.
Payment Collection & Assignments Coordination
This process is about systematically managing payments received from patients for healthcare services. The payments are assigned to specific accounts, considering outstanding balances and insurance coverage. Healthcare providers must also communicate with patients about their financial responsibilities, payment options and plans.
Patient Check-out
This is the final phase of a patient’s visit and time to pay for the medical services. This process includes clearing any unpaid balances, gathering copayments or deductibles, and giving the patient a clear breakdown of the services provided along with the related costs. Medical providers verify insurance and summarize how much the patient needs to pay.
Every part of this process highlights the importance of accuracy, transparency, and following the rules in healthcare finances. As tech evolves and regulations change, quality payment systems become even more essential. In the end, well-managed billing software keeps hospitals financially strong and increases patient trust by making billing more transparent and patient-centered.
Key Features of Hospital Billing Software
Hospitals with advanced billing software considerably reduce billing errors. The functionality of such systems automates many billing management processes. As a result, medical staff and insurers can focus on decision-making while the software handles patient data, insurance plans, and coding. More about the must-have features that your medical billing team will use below.
Pre-Enrollment for Patients
Pre-enrollment features allow patients to share essential information before they even set foot in the healthcare organization. That’s how medical facilities can collect patient details, insurance info, and medical history in advance. Pre-enrollment speeds up the registration process, reduces wait times, and increases the front desk efficiency.
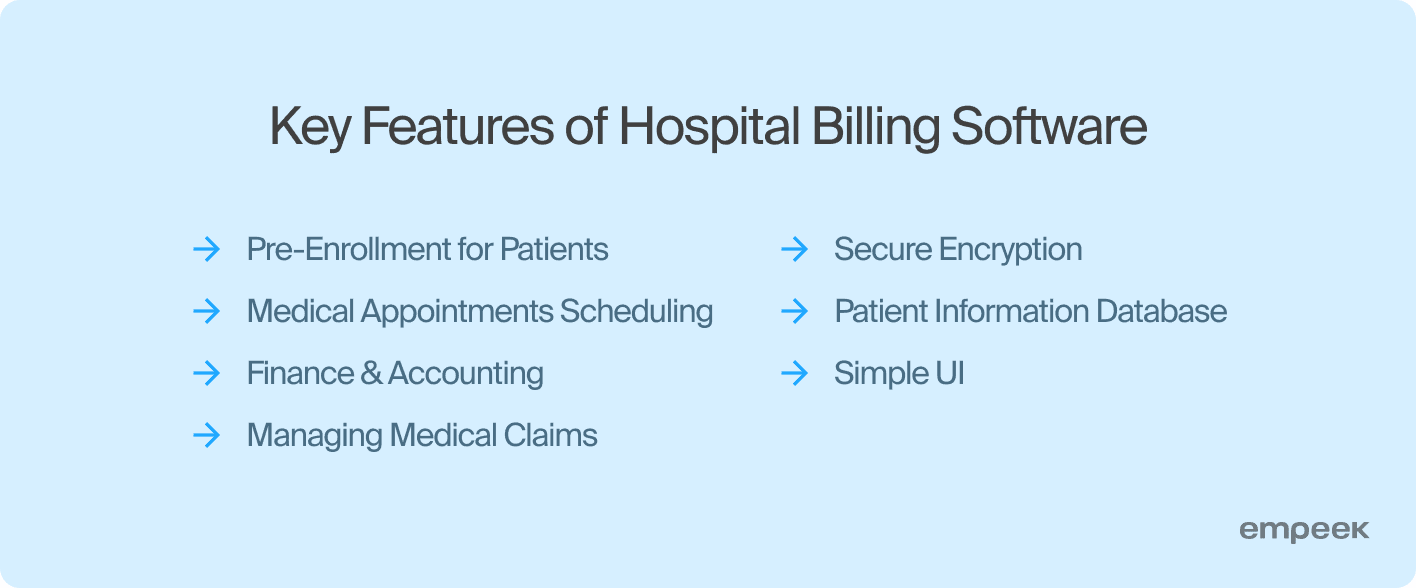
Medical Appointments Scheduling
Scheduling provides a clear and organized way to handle appointments—allowing staff to manage doctors’ schedules, patient visits, and even room availability. It keeps everything flowing smoothly and helps avoid billing mistakes resulting from poor appointment scheduling.
Finance & Accounting
Integral to hospital billing software, the finance and accounting component encompasses the core of billing operations. The financial tracking tool keeps tabs on every transaction, processes invoices, accepts payments, and generates financial reports. It’s like the backbone of the hospital’s financial health, making budgeting easier and giving a clearer picture for future financial planning.
Medical Claims Management
This feature streamlines claim management, including creating and submitting claims to insurance companies. Automation in claims processing is a lifesaver. It reduces manual mistakes, ensures compliance with current rules, and provides real-time updates on denied or rejected claims. That way, your billing team can fix issues quickly and keep the cash flow steady.
Secure Encryption
In an age where data breaches are costly and all too common, secure encryption is non-negotiable. With this feature, security is top-notch, ensuring patient data and financial information are fully protected as it moves through systems. With strong encryption, healthcare providers can build patient trust while staying compliant with privacy laws like HIPAA.
Patient Information Database
A comprehensive patient information database is the memory center of hospital billing software. This means secure storage for patient records, treatment histories, billing info, and insurance data. Having quick access to this information not only makes billing more accurate but also improves personalized patient care.
Operation Simplicity
The best hospital billing software should feature an intuitive interface that’s simple to operate. The software’s user-friendly design means less training for staff, fewer billing errors, and more streamlined day-to-day operations. A user-friendly medical billing system empowers staff to focus more on patient care and less on navigating complex software.
Hospital billing software has become an essential part of healthcare management. It simplifies complicated billing tasks, ensures compliance with regulations, and supports the revenue cycle from start to finish. Such functionality helps hospitals stay financially strong and improve patient satisfaction by making billing clear and accurate. Most financial operations become automated, which reduces the risk of errors and the load on administrative teams.
The Development Stage
A new hospital billing software implementation is akin to preparing for a marathon; it requires careful planning, coordination, and stamina. You should work with healthcare engineering specialists who speak medical coding fluently to provide valid software advice and understand your medical practice.
Below are the main steps you will go through while implementing medical billing software in a healthcare setting:
| Stage 1: Discovery | The discovery stage should be the first step in the implementation of hospital billing software. Beyond just understanding what’s needed, healthcare providers also examine their current systems, workflows, and problem areas. They team up with IT experts to identify the gaps and what specific issues the new software needs to solve. This thorough approach ensures the new system fits the unique needs of the healthcare facility, setting the stage for a smooth and effective rollout. |
| Stage 2: Planning | In the planning stage, the project team comes together to create a detailed software implementation roadmap, outlining a project timeline, budget, and resource allocation. They also run risk assessment and management plans to anticipate potential challenges. This phase results in the master plan, ensuring every step of the implementation process fits perfectly with the hospital’s big-picture goals. |
| Stage 3: UI/UX Design | The UI/UX design phase allows you to create an intuitive and user-friendly interface tailored specifically for hospital billing software. Designers focus on making complicated billing systems simpler and easier to use, cutting down on staff training time and lowering the chance of mistakes. The result is an interface that not only meets the tech requirements but also keeps the user in mind, making the software more effective and leaving healthcare workers more satisfied. |
| Stage 4: Development & Testing | The development phase involves bringing the software to life based on the specifications established in the previous stages. At the same time, thorough testing takes place to make sure the software runs smoothly. Quality assurance includes checking each part individually, looking at the overall performance, and testing usability. Developers and quality assurance teams work side by side to deliver a reliable and bug-free product. |
| Stage 5: Integrations | The software must seamlessly communicate with other hospital systems for accurate and efficient data exchange. Easy integration is key for smooth billing and better patient care. The engineering team connects the billing software with the existing system and thoroughly tests everything to ensure data flows smoothly between them and create a fully connected healthcare environment. |
| Stage 6: Release | The release phase marks the much-anticipated moment when the billing software goes live. This critical step is taken after extensive testing and staff training to ensure a smooth start. Often implemented in stages, starting with a pilot program, the release phase allows for careful management of the transition. This way, the engineering team can identify and address any remaining issues before full-scale deployment. |
| Stage 7: Maintenance | Post-implementation, the maintenance stage is dedicated to ongoing support, troubleshooting, and updates that keep the software running efficiently and securely. At this stage, the hospital and the software provider should cooperate closely to ensure the system stays flexible and responsive to the hospital’s evolving needs. Regular updates and maintenance will guarantee the hospital billing system works effectively in the long term. |
Tech Future of Hospital Billing
Just like other healthcare solutions, hospital billing software becomes more sophisticated each time a new technology like AI or blockchain emerges. The efficiency of healthcare providers’ operations depends on the software they implement and the level of automation it brings. Therefore, vendors and healthcare providers invest in innovative billing software solutions, ensuring accuracy and reliability.
AI and ML are among the most trendy technologies adopted for hospital billing. They enable predictive analytics that makes the billing process more efficient and identify issues before they become major roadblocks. Blockchain technology reshapes healthcare data security and transparency, offering a safer and more trustworthy way to protect sensitive financial information. On top of that, better system interoperability enables healthcare systems to communicate easily, ensuring smooth data sharing that’s important for efficient billing.
New patient engagement tools are another game changer. They offer a more transparent and patient-friendly billing experience with features like personalized portals, real-time updates, and easy payment options. Using such tools, patients can better understand and manage their financial responsibilities.
These technologies will optimize revenue management and enable patient-centered, transparent, and tech-savvy care. Healthcare providers can become more cost-efficient and focus on patient experience thanks to automated billing operations.
Discover: 5 Telehealth Trends to Follow in 2024 And Beyond
Final Thoughts
Implementing a hospital billing system is a necessity for most large and medium practices that want to optimize their finance management. The primary choice is between an off-the-shelf and a custom-based software. While ready-made systems are a quick solution, custom billing systems are more efficient, secure, and patient-centered.
Whether you need assistance with hospital billing software integration or development, Empeek can help. Contact us for a quote and learn how our tech expertise can serve you.








