IoT-powered medical devices are set to redefine modern healthcare. These smart tools—equipped with sensors, cloud connectivity, and data analytics—exist to monitor vital signs in real time, to optimize hospital workflows, and to enable precision medicine.
The numbers prove this revolution is accelerating: global adoption of medical IoT devices will jump from 42.2 million users (2024) to 67.5 million by 2028, fueled by the urgent need to manage chronic diseases and aging populations.
But beyond statistics, what makes these devices truly transformative? Their ability to deliver:
- To detect cardiac irregularities before symptoms appear (e.g., implantable loop recorders)
- To prevent medication errors (e.g., smart IV pumps)
- To empower patients to manage conditions remotely (e.g., connected insulin pens)
In this article, we examine how medical IoT devices work to improve outcomes, with real-world examples that Empeek delivered and that already changing standards of care.
What are IoT Medical Devices?
IoT Medical Devices are specialized devices connected through the Internet for quick data exchange. They have smart sensors to collect biometric data and require software that instantly processes the information. The combination of custom software and sophisticated hardware designed for low power consumption allows IoT devices to analyze healthcare data in real time and work independently for prolonged periods.
Medical devices enhanced with IoT technology include wearables, hospital equipment, smartwatches, IoT implants, ECG, glucose monitoring devices, and smart pills. Medical IoT devices can continuously monitor patients’ well-being and warn healthcare providers about changes. They allow medical staff to promptly adjust a treatment plan, schedule a remote consultation, or hospitalize the patient to prevent health deterioration.
Benefits of IoT Medical Devices
The Internet of Medical Things makes self-monitoring more accurate and accessible, while IoT in hospital management improves hospital efficiency and many medical procedures, from diagnostics to surgeries. The major benefits of interconnected healthcare include:
Better patient monitoring inside and outside a hospital environment
Smart wearables and trackers can help transmit patient data from their homes to doctors and hospital staff. This technology reduces unnecessary follow-up visits, helps doctors know more about potentially dangerous patient conditions, and provides advanced diagnostics.
Help people with chronic illnesses and the elderly.
IoT medical devices can track health indicators remotely to detect critical situations and send alerts for medical help in an emergency.
Internet of Things for medical research support
Since connected healthcare devices generate tons of valuable health data, they enable advanced data analysis, which, in turn, improves the quality of treatment and pushes for technological advancements and medical research.
Operational efficiency
IoT increases operational efficiency by enabling real-time monitoring of hospital operations on a larger-scale level. This helps to make data-driven decisions and improve resource management. For example, hospitals can track medical equipment or medical supplies with IoT systems for optimized use and cost optimization.
Decreased medical equipment downtime
The predictive maintenance feature based on machine learning in connected devices notifies healthcare workers of any unusual equipment performance so they can take a closer look. They can organize an urgent inspection and repair the machinery before a serious breakdown or before it starts to provide inaccurate data.
Enhanced inventory management
Thanks to IoT, hospitals can easily track many assets: drugs, inventory, hardware, etc. This way, it’s easier to manage hospital operations, allocate the right resources, and ensure the equipment is available when needed. Asset tracking with the help of RFID tags or other types of smart labels is applied to surgical tools, inventory, laundry, or any other piece of equipment.
Virtual medical documentation
Medical IoT solutions like Augmedix are designed to improve clinician productivity by automating visit data, capturing dictation, generating suggestions, and synchronizing with patient records. Such AI-powered solutions are extremely helpful for telemedicine sessions, allowing for automated record-keeping.
By connecting IoT and medical devices, healthcare organizations can facilitate treatment procedures for patients and health professionals. Due to their data-centric approach, such devices increase treatment accuracy and identify valuable disease patterns demonstrated by each patient.
IoT Medical Devices for Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote patient monitoring devices include different wearable devices that can continuously measure patient vital signs. As the name suggests, patients can carry this type of medical solution around their wrists or on their fingers. Remote patient monitoring devices monitor heartbeat, temperature, glucose levels, pressure, and oxygen levels. Doctors can check on their patients whenever any of these signs change and cause concerns.
Medical IoT Devices Examples
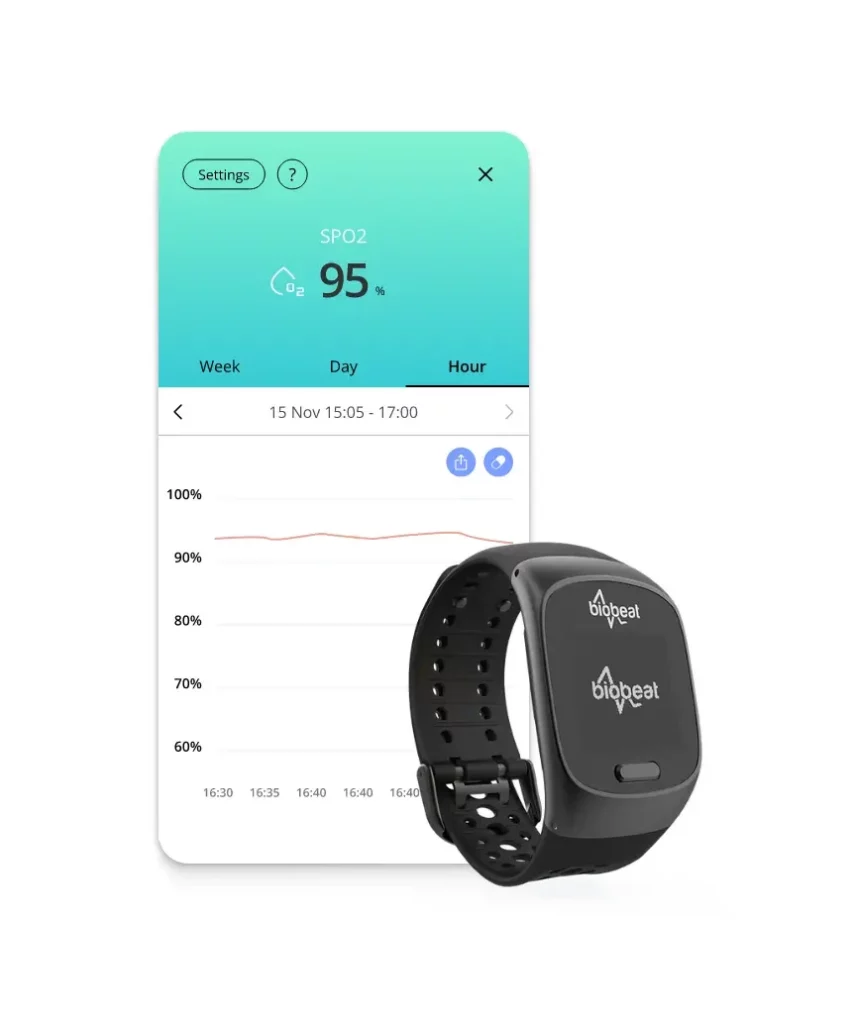
- The BioBeat wristwatch uses advanced PPG sensors and AI-powered analytics to provide real-time health metrics tracking. Empeek developed a mobile app that connects with a custom-designed smartwatch to detect early changes remotely and ensure timely interventions. Data security compliance with HIPAA and GDPR standards enables safe sensitive data transmission to a cloud-based platform.
- Wearable blood pressure tracker WBP202 allows continuous monitoring with a comfortable-to-wear device. It also detects irregular heartbeats and supports a wide-range D-ring cuff. Patients can recharge the battery and choose different cuff sizes depending on their needs.
- The Navigine Patient Tracking System enhances hospital efficiency and patient safety through real-time location tracking. Using technologies like indoor positioning and real-time location systems (RTLS) it allows for continuous monitoring of patient movements and conditions, reducing the risk of losing the patient. This might be especially useful for senior care facilities. Patients receive a bracelet with a tag containing key medical information. Hospital sensors detect and transmit the data from the bracelet to a cloud-based system. Healthcare staff can access real-time updates, ensuring better coordination and minimizing wait times.
IoT Medical Devices for Chronic Disease Management
Another way to use connected medical devices is for chronic disease management, such as heart or glucose monitoring. Since chronic diseases require constant attention, continuous patient monitoring via IoT systems is a go-to solution for hospitals and at home. Patients and doctors can collaborate to improve treatment outcomes thanks to real-time data. This promotes better self-care among patients and improves doctor’s understanding of the disease course.
IoT devices examples
- An AI-based heart monitoring system allows patients and medical staff to manage heart health remotely. It relies on a neural network model to automatically analyze and classify heart events, reducing false alarms during continuous cardiac monitoring. This way, healthcare providers can take on critical cases faster and improve patient outcomes. Empeek designed the entire platform, including proprietary ML algorithm that detects abnormalities and suggest diagnosis.
- MyGlucoHealth is a blood glucose monitor designed to simplify diabetes management through real-time data tracking. This device is powered with Bluetooth technology and connects to a secure online platform, which doesn’t require manual logbooks. The system allows patients to upload and track their glucose levels while providing healthcare professionals with instant access to data. Automated reminders help maintain regular testing, and alerts can notify doctors of level fluctuations.
- The Lung Monitor BT Smart is a portable solution enhanced with Bluetooth designed for remote lung condition tracking. It supports patients with chronic respiratory conditions like cystic fibrosis, COPD, and post-transplant recovery. The device is comfortable for use at work, home, and healthcare settings. It transmits real-time data to medical professionals via different operating systems. Features include dual-mode Bluetooth, automatic best-value storage, a blow indicator, and an intuitive display for efficient and accurate monitoring.
IoT Medical Devices for Patient Safety
Another reason to use IoT in medical devices is to ensure patient safety in healthcare facilities and at home. If a hospital establishes hand hygiene monitoring devices, they can improve tidiness and reduce the risk of infection spread. Medical professionals can also prescribe ingestible sensors that track a patient’s medication habits. Innovative safety measures minimize oversights in treatment routines.
IoT Devices Examples
- An IoT hand hygiene device like the one by CenTrak can help hospitals track whether employees follow hygiene routines. The sensors within individual workers’ badges detect their visits to hand washing stations. The administration can access healthcare professionals’ reports and check whether they meet hand hygiene standards. This system reduces the spread of infection and automates auditing, which leads to improved patient care.
- Digital pill systems (DPS) that help improve medication adherence also rely on IoT. A system checks whether patients take their medications according to the treatment plan. The digital pill transmits the medical data in real-time via a tiny radiofrequency emitter activated after swallowing. It transmits the data to a Reader device, which then sends it to a cloud platform accessed by healthcare providers. The pill covered in food-grade epoxy is safe for the patients. Moreover, the device can send reminders if the patient forgets to take medications, which improves disease management.
- The Q-Collar is an FDA-approved device designed to help protect athletes from brain injuries caused by frequent subconcussive impacts. Worn around the neck, it produces gentle pressure to the jugular veins, boosting blood flow in the brain to reduce excessive movement upon impact, the primary cause of brain injury. This noninvasive remote monitoring solution functions similarly to a seatbelt, helping to stabilize the brain during workouts. Studies indicate that jugular compression with the Q-Collar reduced neuron and axon damage by 83%.
IoT Medical Devices for Advanced Care
Advanced care involves constant patient support if they have life-threatening or chronic conditions that are sensitive to timely treatment. Medical device IoT expands care possibilities by providing patients with a small personal care advisor that monitors their treatment habits. Moreover, robotic surgery based on advanced IoT technologies is becoming the right hand of surgeons. They can perform complex procedures thanks to the enhanced abilities of IoT robotics.
IoT Devices Examples
- The FindAir System includes smart inhalers that enhance remote asthma and COPD management. Smart inhalers track medication use and record the dosage and time to provide precise treatment insights. The FindAir Asthma Diary App integrates with smart devices, offering medication reminders and trigger analysis to help clinicians understand disease patterns. An online platform enables remote patient monitoring for doctors to identify those who need treatment adjustments.
- Robotic surgery systems like da Vinci or NAVIO improve operation accuracy and patient outcomes since surgeons can rely on a three-dimensional view that helps control specialized robotic tools. Unlike traditional laparoscopic instruments, robotics enhanced with IoT expands the range of motion, making complex procedures easier to perform. This approach also reduces muscle tension during long operations, which leads to fewer complications and shorter recovery times. Additionally, robotic surgery decreases the formation of blood clots by 77%.
- MyDial is a transportable hemodialysis system designed to give patients greater flexibility and independence in managing their treatment. The system doesn’t weigh much and allows users to seamlessly integrate dialysis into daily life without requiring hospital visits. With an intuitive touchscreen, easy installation, and no need for professional skills, MyDial supports bicarbonate dialysis therapy with customizable settings to meet individual patient needs.
Security Challenges in Medical IoT Systems
Given that internet-connected medical devices are vulnerable to hacker attacks and data leakage, it’s a top priority to develop medical IoT solutions with the latest security practices in mind. There are also many standards to comply with, including HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), HITECH (Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act), NHS (National Health Service), and FDA requirements for the US. The FDA conducts cybersecurity assessments and issues warnings to the public about manufacturers and devices with identified vulnerabilities.
These regulations require the integrity and safety of personal health information from medical IT solutions. If a medical device that collects patient data lacks industry standards, the identifiable data can be exposed, leading to fraudulent insurance claims and other consequences.
When creating medical hardware or software for use in healthcare environments, connected medical devices cybersecurity is one of the biggest challenges. Around 1 in 5 connected medical devices use outdated or unsupported operating systems. These include MRI and X-ray scanners. Such vulnerabilities in the IoT medical devices sector can cause critical data breaches. Thus, the demand for healthcare IoT security is very high. Since tracking devices involve a lot of sensitive information, it’s crucial for them to use proper encryption and comply with regulations.
Primary measures to protect IoT medical devices from security breaches include:
- Encryption. The use of cryptography and public key infrastructure is a must for any platform that collects or stores personal health information. Symmetric and asymmetric algorithms applied to IoT can still not guarantee the best protection in real-time: Elliptic-Curve Cryptography and a Hybrid Lightweight Algorithm are more secure for the IoT application in medical devices.
- Network segmentation. Subnet division allows for better control over the network: this way, a locally implemented device for unintended use can’t impact the entire structure.
- Authorization and authentication. Any medical device and the infrastructure it’s connected to should limit access to data at all stages of interaction to prevent interception.
- An orchestrated update process. Updating IoT hardware and software is no easy task and it can expose devices to cyberattacks. Manufacturers and developers should adopt a secure and effective process for updating the system and validating it across all the devices that are in use.
- User instructions. Finally, giving end-users clear instructions on installation, configuration, and access won’t hurt.
Smart healthcare requires enhanced security features to protect patient data from exposure by using built-in security functionality and following safety standards during device development. Additionally, vulnerabilities in the system should be addressed on a regular basis via software and hardware updates and continuous system maintenance services.
Empeek for IoT medical software development
At Empeek, we build HIPAA- and GDPR-compliant healthcare IoT solutions, making sensitive data protection one of our major goals. We’ve been developing medical software for almost a decade and can create custom medical IoT apps or IoT extensions to enhance existing systems.
Empeek delivers custom IoT solutions and services for care providers, healthcare organizations, and wireless medical device manufacturers. We have the expertise to configure advanced software architecture and develop data analysis algorithms that enable IoT medical devices to analyze large volumes of data efficiently. Whether it’s assembling a dedicated team to cover the entire software development life cycle (SDLC) or assisting with specific tasks, Empeek can provide the necessary support to expedite the implementation of IoT for medical devices.
Final thoughts
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) has fundamentally changed healthcare delivery. Today’s connected devices:
- Enable continuous patient monitoring beyond hospital walls
- Reduce preventable medical errors through automated systems
- Empower clinicians with real-time, data-driven insights
Looking ahead, three key developments will shape IoMT’s evolution:
- Miniaturization of wearables for greater patient comfort
- Advanced predictive analytics through AI integration
- Enhanced interoperability across healthcare systems
While security challenges require ongoing attention, IoMT’s potential to shift healthcare from reactive to proactive care is undeniable. These technologies don’t just improve outcomes—they redefine what’s possible in modern medicine.
For healthcare organizations ready to leverage IoT:
Our team specializes in developing secure, compliant medical IoT solutions tailored to your clinical workflow. Contact us to begin your IoMT journey.