Telemedicine technology has become a savior for rural and distant locations without proper access to healthcare services. Before the spread of online consulting, patients and their caregivers had to travel long distances and suffered from limited resources and a shortage of medical facilities. This made simple check-ups and routine consulting challenging to obtain.
Rural telemedicine removes the barriers created by distance and makes healthcare accessible for everyone. A patient can open a laptop or mobile device, schedule a meeting with the preferred doctors, and get consulting, even if they live in a remote village.
Want to know more about rural telemedicine and how it will keep changing? Read our overview to discover the recent trends and high-demand niches.
State of Rural Telemedicine Overview
Rural telemedicine in the United States and globally considerably differs in quality and coverage compared to urban areas. As of 2022, rural regions, comprising 19.3% of the US population, struggled with fewer healthcare providers than urban areas. They have only 13.1 physicians per 10,000 people versus 31.2 in urban settings. Rural residents also report higher rates of fair or poor health.
Besides, rural healthcare faces some infrastructural limitations such as inadequate broadband access. Due to poor internal connection, rural residents cannot always use online consulting effectively. Fortunately, governments and healthcare facilities make steps to expand the telemedicine infrastructure and engage rural residents to join telemedicine programs for achieving equitable access to healthcare services across rural communities.
Despite these challenges, the rural population shows an increasing interest in telehealth solutions (44% of rural beneficiaries used telehealth services) driven by the need for convenient and accessible healthcare options. People who have tried remote consulting share positive reviews and are ready to use it again. Growing telemedicine adoption reduces healthcare disparities across regions and improves patient outcomes.
However, ongoing education and advocacy efforts are still necessary to address concerns about privacy, technological accessibility, and telemedicine integration into routine healthcare practices.
Possibilities of Rural Telemedicine and How It Simplifies Lives
Telemedicine cannot replace in-person visits entirely and doesn’t have to, however, there are many benefits of telehealth in rural areas. It improves access to different specialists, reduces isolation, and enables remote patient monitoring. Here are the main advantages of telehealth for patients and healthcare providers.
Possibilities for Patients
| Increased Access to Specialists | Patients in rural areas can consult with specialists without the need to travel long distances, improving access to specialized healthcare services. |
| Timely Medical Advice | Telehealth enables patients to receive quicker consultations and second opinions, leading to more timely medical advice and interventions. |
| Access to Wellness Programs | Programs for smoking cessation, nutrition, and weight loss become more accessible through telehealth platforms, promoting overall wellness among rural populations. |
| Improved Chronic Disease Management | Telehealth facilitates regular monitoring and follow-up care for chronic diseases, leading to better disease management and patient outcomes. |
| Improved Mental Health Care | Rural telepsychiatry provides easier access to mental health services, addressing a critical need in rural areas where mental health providers are often scarce. |
| Reduced Hospital Visits | Better remote patient management through telehealth results in fewer emergency room visits and hospitalizations, easing the burden on rural healthcare facilities. |
Possibilities for Providers
| Better Collaboration | Providers in rural areas can collaborate with larger healthcare institutions for better patient care, leveraging the expertise and resources of these institutions. |
| Efficient Use of Resources | Telehealth helps optimize providers’ time and allows them to manage more patients efficiently, improving the overall healthcare delivery in rural areas. |
| Remote Monitoring | Providers can monitor chronic conditions remotely, which improves patient outcomes by allowing for continuous and proactive health management. |
| Reduced Isolation | Telemedicine reduces the professional isolation of rural healthcare providers by connecting them with peers and specialists, fostering a supportive professional network. |
| Continuing Education | Telehealth platforms offer more opportunities for training and continuing education, keeping providers updated with the latest medical knowledge and practices. |
Telemedicine is a powerful tool that addresses many challenges rural telehealth systems face. It makes healthcare services more accessible and allows patients to receive timely medical advice regardless of their location. On the other hand, rural telemedicine also considerably simplifies the lives of medical staff. Providers can work more efficiently, cover more patients with their services, and optimize the load on doctors.
Limitations and Disadvantages of Telemedicine in Rural Areas
While telemedicine is a blessing for many patients in rural areas and providers who aim to serve them, it still entails challenges. You must consider them while implementing telehealth for rural areas to make the services more accessible and convenient.
Limitations for Patients
- Limited Internet Access
Many rural areas lack reliable high-speed Internet. - Technology Barriers
Some patients may struggle to use telemedicine platforms due to poor tech literacy. - Privacy Concerns
Ensuring patient data confidentiality and security in home settings can be difficult. - Lack of Personal Touch
Patients may miss face-to-face interaction and hands-on care.
Limitations for Providers
- Licensing and Reimbursement
Navigating different state regulations and insurance policies can be difficult. - Technical Issues
Providers may face challenges with telehealth interoperability and connectivity. - Workflow Integration
Incorporating telemedicine into existing practices requires software engineering services and the charge in standard operational workflows. - Limited Physical Examination
The inability to perform physical exams in person can limit diagnostic accuracy.
Fortunately, most of these disadvantages of telemedicine in rural areas aren’t critical, and you can handle them with the right approach. As Internet access improves worldwide, technological literacy also increases, eliminating limitations on the patient’s side. At the same time, healthcare providers can deal with the challenges through professional consulting and by hiring a telehealth engineering partner to help with software integration.
Where is the Space for Growth? 6 Tech Solutions To Implement for More Efficient Rural Telemedicine
Some technologies and approaches are particularly effective for rural telemedicine and demand in this healthcare field. This chapter explores six tech solutions poised to propel rural telemedicine forward, offering insights into their applications and market demand.
If you are considering adopting telehealth for rural areas or investing in rural telemedicine software development, these trends can guide you in your choice.
1. AI and Gen AI Solutions
Given the high cost of healthcare services and workforce shortages, especially in rural areas, Gen AI has a huge transformative potential. Adopting AI can reduce administrative costs by 13-25%, lower medical costs by 5-11%, and increase revenue by 3-12%. However, the healthcare industry adopts AI slower than many other sectors due to challenges such as data preparation, infrastructure needs, and talent scarcity.
Speaking of AI, the major opportunity is unstructured data processing and automation. Yet, to fully unlock this potential, healthcare leaders must address several key challenges, including improving data management, investing in the necessary infrastructure, and finding an experienced AI provider.
Your next read: AI-powered Heart Monitoring: A Case Study in Improved Efficiency & Accuracy
2. Prescription Management Solutions
Effective prescription management is a cornerstone of chronic care management, ensuring patients adhere to their medication regimens for optimal health outcomes. This is particularly important for managing chronic conditions in patients from rural areas who face limited face-to-face care options.
For example, for chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes and obesity, GLP-1 drugs have recently appeared as a transformative treatment option. The eligible patient population for GLP-1s is among the largest for any new drug in decades. However, consistent adherence is crucial, and studies show poor persistence rates. The GLP-1 market expansion underscores the importance of preventive care and has driven telehealth growth. Despite high annual costs ($12,000-$16,000 per patient annually), GLP-1s highlight the need for improved prescription management solutions to ensure adherence and cost-effectiveness, transforming healthcare models and emphasizing cost management strategies.
Learn more about medication management: Best Pill Reminder and Medication Tracker Apps for Prescription Compliance
3. Elderly Care Software
Digital technologies can enhance interactions between older individuals and healthcare services across different stages of care pathways. A good example is structured telephone support for heart failure patients which has shown a notable 15% decrease in admissions.
The main problems with digital solutions for older adults are accessibility and ease of use. Elderly patients often lack digital literacy or adequate access to technology. This digital divide may prevent equitable access to healthcare innovations among elderly populations. It highlights the need for inclusive design and user support to ensure all individuals can benefit from telemedicine advancements.
4. Asynchronous Care
1 in 4 US rural residents still lack a stable internet connection, making alternative methods to telehealth video consultations essential. Asynchronous care solutions, such as secure messaging, email consultations, and offline data collection, allow medical staff to consult patients even when they cannot have an online call.
Therefore, if you consider investing in telehealth for rural areas, you should view asynchronous communications as your primary channels to stay in touch with patients. This will allow you to adapt to the limitations of people living in remote areas.
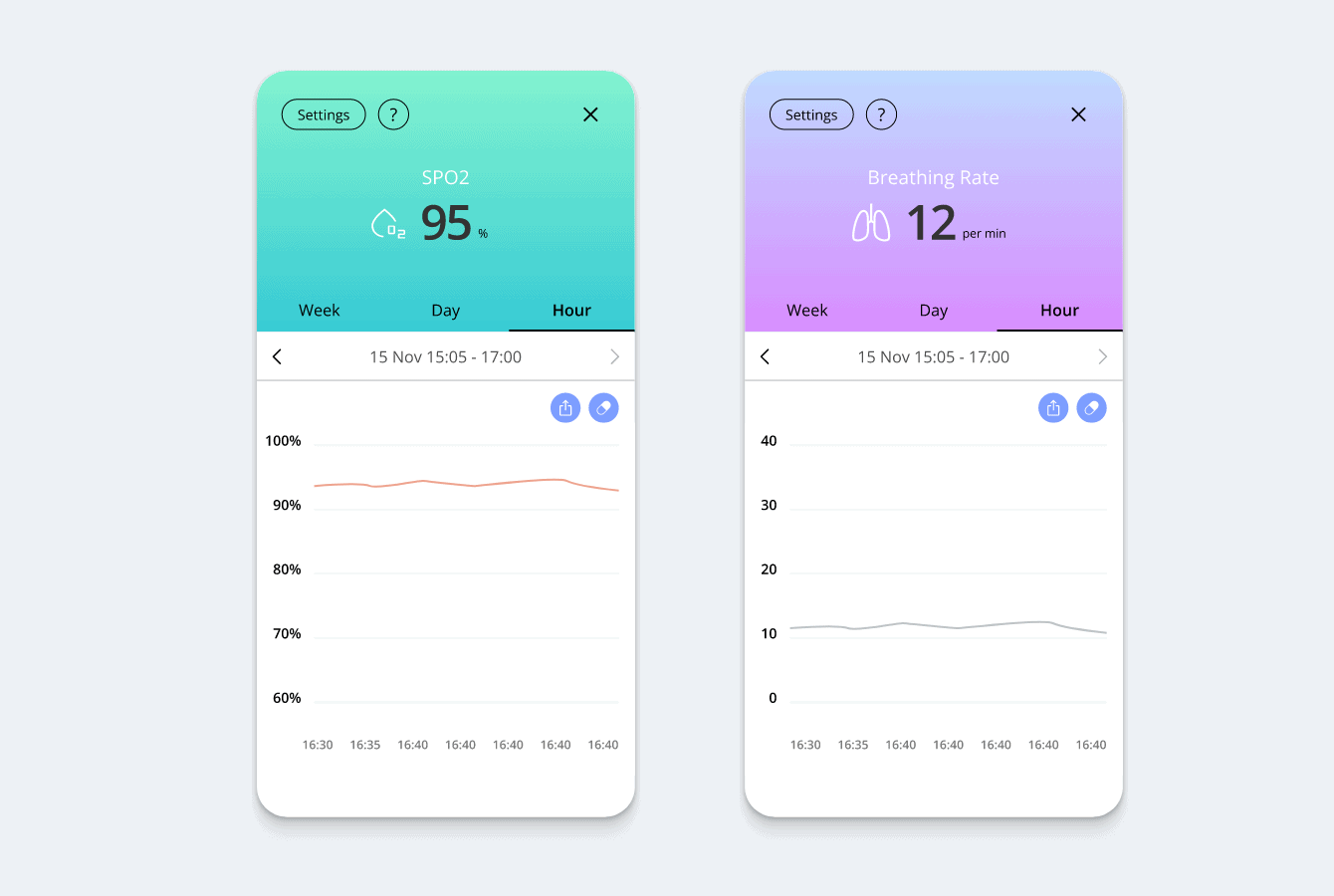
5. Remote Monitoring Devices
Remote monitoring in healthcare, particularly in rural settings, is becoming increasingly prevalent and beneficial. It involves the electronic transfer of self-reported or biometric data such as oxygen saturation, pulse rate, and blood pressure remotely using devices located in patients’ homes or placed directly on users. Remote monitoring as telehealth for rural areas enables continuous health supervision without frequent in-person visits. This is crucial in rural areas where healthcare facilities may be far apart, and transportation can be a barrier.
6. Telepharmacy
Telepharmacy can ensure timely access to pharmacists and prescription medications in remote, rural communities. One effective model involves pharmacists providing consultations and supervision via live video conferencing while pharmacy technicians handle the physical dispensing of medications at remote sites.
This approach has improved patient education and counseling effectiveness. Another model includes automated drug dispensing technologies, such as kiosks, which enhance accessibility in areas where traditional telepharmacy setups may not be feasible. For instance, MedCentre kiosks in Ontario integrate prescription scanning, patient-pharmacist teleconferencing, and automated dispensing, demonstrating high consumer satisfaction.
Each of the listed solutions shows how much potential telemedicine has to improve access to quality care for underserved populations. By using the transformative potential of these tech solutions, healthcare providers can build more efficient, inclusive, and resilient healthcare systems for rural communities worldwide. On the other hand, companies investing in rural telemedicine software development can enter a relatively free niche with ample opportunities.
Empeek for Rural Telemedicine Development
Empeek is an engineering company that specializes in healthcare software development and telemedicine platforms in particular. We can assist you with end-to-end development of a remote consulting platform for rural areas or help implement and customize one of existing solutions in your practice. Our team has designed a scalable telehealth platform for behavioral health, IoT real-time monitoring systems, and other projects.
Schedule a consulting session to learn more about how our services can support your practice in implementing rural telemedicine.
Conclusion
Rural telemedicine is a new, powerful trend that transforms healthcare delivery in underserved communities. It makes quality care more accessible, enhances collaboration among healthcare specialists, and improves patient care. Despite significant benefits, telemedicine in rural areas also brings its challenges, including limited internet access, technological barriers, and integration complexities. So, you must be ready to handle the obstacles and have a reliable technological partner to help with telemedicine implementation.
Contact Empeek to learn what it takes to implement rural telemedicine in your case. We will analyze your request to provide a project estimate and development roadmap.