Artificial Intelligence provides physicians with data-driven insights to diagnose patients, plan treatments, and manage care. Medical software companies also widely use AI to automate personnel management, training, and billing.
According to MarketsandMarkets, the value of AI in the healthcare market is projected to exceed $31 billion by 2026. AI shows promising results in different domains, including medical imaging analysis, automation of healthcare operations, personalized medical care, and smart RMP devices. It can help fix problems like misdiagnosis, which is a big issue given that 7.4 million misdiagnosis errors happen every year.
Learn more about the application of AI in healthcare in our blog post.
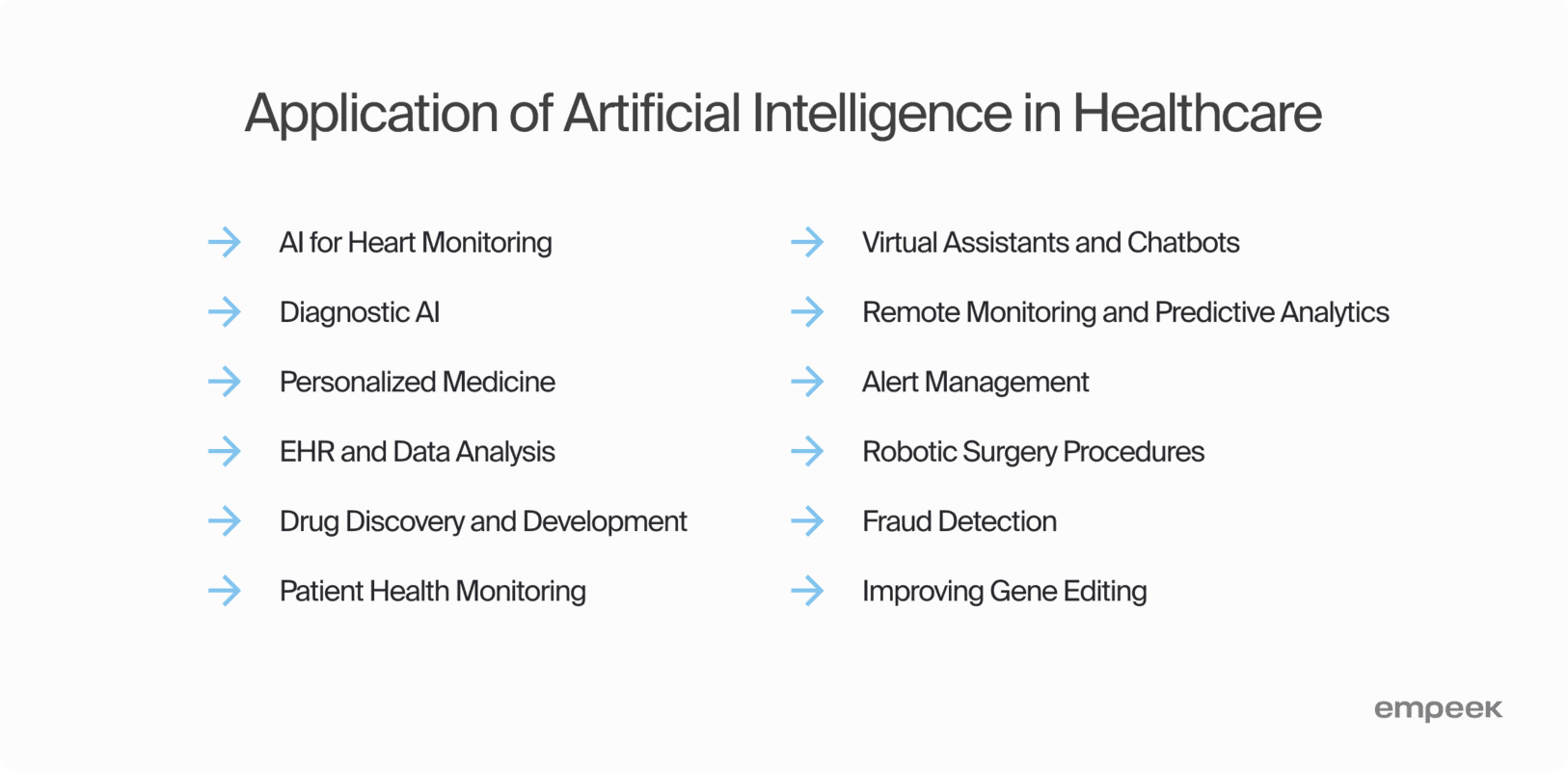
Applications of AI in Healthcare
The British NHS is an excellent example of the effective use of AI algorithms. They help the organization improve healthcare services by assisting in the following:
- X-ray image analysis. AI healthcare apps support radiologists with decision-making and give them more time to interact with patients. This way, doctors can handle more cases in a day.
- Home-care services: Remote monitoring AI medical applications collect and monitor vital data, transferring it to the corresponding medical specialists. This way, people can receive quality care from their homes.
- Quick brain scanning: Algorithms provide insights that help doctors make quick decisions in cases that require rapid action.
These are just a few of AI in healthcare examples. To understand how medical facilities adopt and benefit from innovations, let’s examine 12 common applications of artificial intelligence in healthcare more closely.
Healthcare AI Applications for Heart Monitoring
Artificial intelligence applications in healthcare are changing heart monitoring, providing instant results on health activities. AI-based devices can detect irregularities, diagnose heart problems, and notify doctors about potential risks early on. Neither the patient nor medical staff have to manage the process since a cardiac monitoring device continuously tracks and analyses cardiovascular data independently.
Empeek has created an AI-based platform for real-time heart monitoring with minimum human intervention. Our developers combined big data and machine learning algorithms to create a system that recognizes and classifies heart events. Learn more about how it works in the case study.
Diagnostic AI
Diagnostics based on AI and ML provide medical professionals with accurate data analysis to detect patterns and dependencies. Medical staff get real-time insights that can support or question their treatment decisions.
AI and ML also solve the problem of legacy health data, turning obsolete records into valuable information. Hospitals annually perform 3.6 billion imaging procedures, generating a massive amount of data, a large share of which resides in the storage. Machine Learning helps to structure and use this information for more precise diagnostics and scientific research. As a result, doctors can rely on previous cases and reliable findings while diagnosing new patients.
IDx-DR is one of such top AI applications in healthcare that detects diabetic retinopathy. IDx-DR analyses retinal images captured by a specific retinal camera without human intervention. The system provides rapid results, typically within minutes, and has shown high accuracy in clinical trials.
Personalized Medicine
A personal approach is crucial to viewing each patient as unique and assigning treatment that suits them best. AI facilitates this customer-centric approach by automatically processing large data volumes and turning them into informative insights.
Algorithms can accurately analyze genetic information and medical history to tailor separate and individual treatment plans. They can also recommend specific medications while considering patient-specific characteristics to prevent side effects.
23andMe is a great example of a company that uses AI in personalized healthcare diagnostics and DNA analysis. It takes a saliva sample of a consumer’s DNA to provide information on how their genetic structure might affect the response to some medications. Some reports include clopidogrel, a blood thinner; omeprazole, which relieves acid reflux; ondansetron, which is for motion sickness; and simvastatin, which lowers cholesterol levels. This service can tell if one has increased chances of experiencing side effects or reduced effects of these medicines.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Data Analysis
The everyday work of a healthcare specialist includes collecting, managing, and analyzing massive volumes of data. It is daunting, and mistakes are always possible due to tiredness or distraction. AI-driven solutions come in handy in these situations, completing routine tasks automatically.
AI models thoroughly analyze electronic health records (EHR) and other clinical data sources to detect patterns. Healthcare specialists then make conclusions and use these insights in treatment planning.
AI systems have strong encryption and authentication measures to meet HIPAA laws, assuring data privacy and security. Therefore, healthcare providers don’t have to worry about regulatory compliance when implementing innovative software.
Drug Discovery and Development
The usual drug discovery process is complicated and time-consuming, but AI algorithms can reduce the time needed to identify drug candidates and make predictions. AI analyzes data to detect promising molecules, expediting the drug development timeline.
PathAI uses AI for drug discovery and development. The company’s AI-powered pathology platform, AISight, has rich functionality for pharmaceutical research and clinical trials.
PathAI helps researchers analyze tissue samples with advanced ML algorithms to enable more accurate biomarker discovery and validation. The platform also optimizes clinical trials through improved patient selection and stratification, potentially increasing trial success rates.
Virtual Assistants and Chatbots
AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots transform patients’ communication with healthcare organizations. Patients can ask general medical questions, schedule appointments, and receive direct medical guidance in real-time. These tools help educate patients, respond to general questions, and reduce the workload on medical specialists.
Most health care chatbots are free for patients, though some charge for extra features. Providers may prescribe these apps, and they can be covered by insurance or licensed to providers.
Companies like Ada Health provide a virtual health assistant that uses AI to analyze symptoms. Based on this analysis, it offers insights and guides users toward relevant medical resources. While virtual assistants are easy to use and convenient, they can not replace in-person medical consultations for serious health concerns.
Remote Monitoring and Predictive Analytics
AI can spot trends and forecast possible health risks by analyzing patient data in real-time. This proactive strategy improves patient care, lowers hospital readmissions, and helps prevent the onset of serious illnesses. That’s how AI improves overall patient outcomes and highlights the value of predictive treatment.
Numerous wearable devices with AI algorithms, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and glucose monitors, are available today. According to GMI, the wearable AI market in healthcare is projected to reach USD 260.29 billion by 2032. Smart wearables can continuously track heart rate, oxygen level, sleep cycles, and blood pressure to inform users and medical staff about deviations.
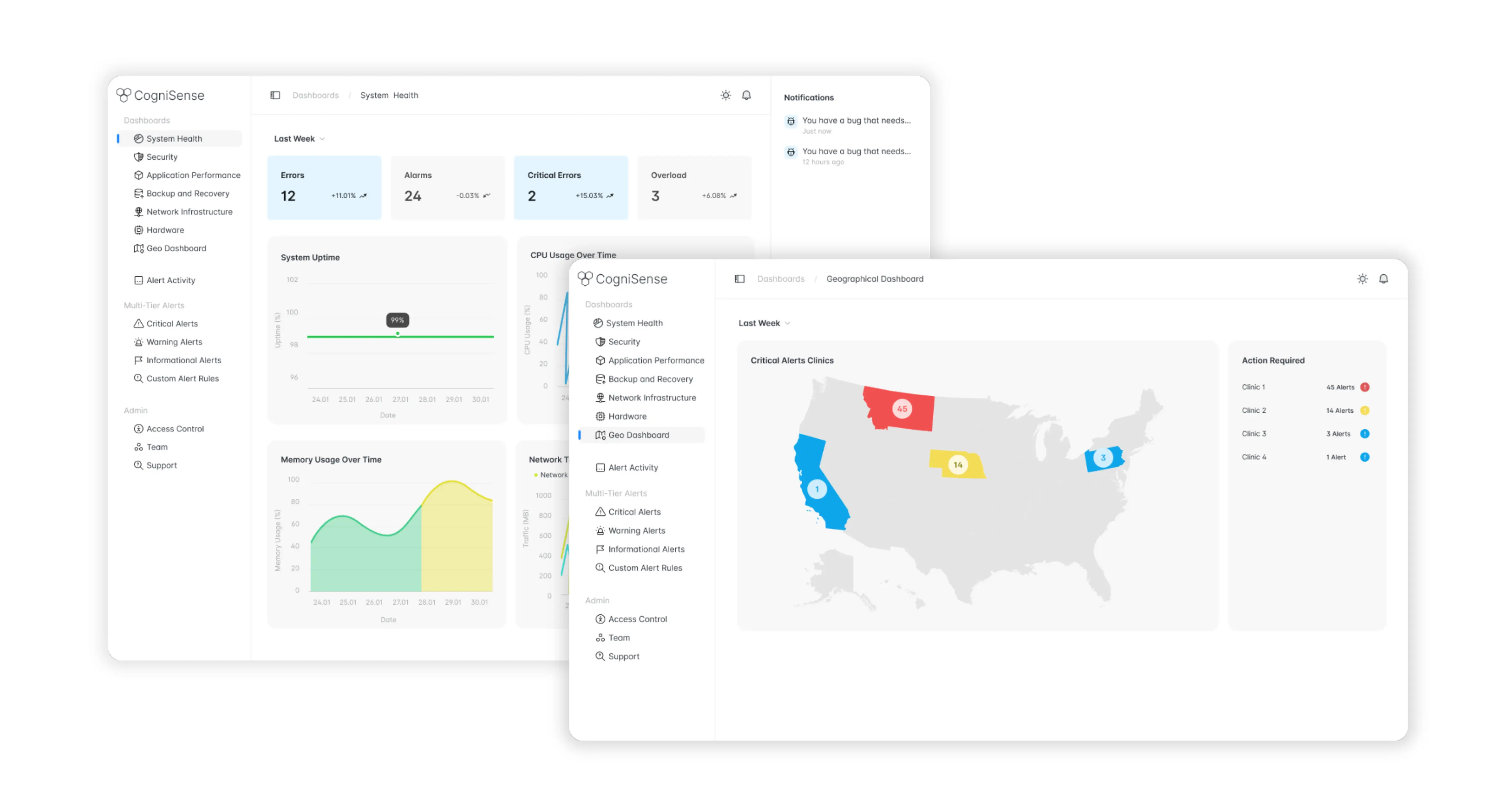
Alert Management
AI-powered alert management in healthcare is revolutionizing how doctors respond to patient health changes. AI smart alerts help analyze patient data in real-time and recognize risks before they become serious problems. This allows healthcare providers to intervene early in a situation.
A study at Mount Sinai Hospital found that patients whose care teams received AI-generated alerts about adverse health changes were 43% more likely to receive timely escalated care and significantly less likely to die. The AI alerts showed better results than traditional manual methods like the Modified Early Warning Score in accurately predicting patient decline.
Empeek developed an AI-powered alert management system that classifies and prioritizes alerts from various data sources. It uses pre-trained models to categorize and summarize notifications while ensuring data privacy. Such software significantly reduces manual review time and optimizes outline operations.
Robotic Surgery Procedures
Robotic surgery has become more sophisticated, and AI implementation considerably increases surgical precision. It analyzes patient data and images in preoperative planning to help surgeons plan procedures more effectively.
AI technologies also help manage waiting lists by prioritizing patients based on severity. This way, hospitals can schedule higher-risk patients sooner. Additionally, AI helps optimize operating room schedules and resource use, making the surgical process more efficient.
One of the great examples of medical AI applications is the intuitive Surgical da Vinci system that integrates AI and robotics in surgical settings. The surgeon’s console gives a doctor total control of the instrument on each arm. It allows surgeons to view the surgical field in 3DHD and is equipped with a built-in innovation: tremor filtration.
Fraud Detection
Healthcare insurers use AI and ML to identify fraudulent activities and assign risk scores to claims. These technologies scan large volumes of claims data to catch suspicious patterns that might indicate fraud. They quickly flag questionable claims before they’re paid out, helping insurers prevent financial losses and saving time on investigations.
AI systems also rate claims based on risk, considering things like the provider’s history or the type of treatment. Thanks to this, investigation teams can take a closer look at high-risk claims and detect fraud faster and more effectively.
One of many examples of AI in healthcare fraud detection is Healthcare Fraud Shield (HCFS), which recently launched FWA360Leads. This AI-powered tool automatically identifies fraud, waste, and abuse leads, optimizing the fraud detection process. It enhances lead value, reduces false positives, and increases operational efficiency for healthcare insurers.
Patient Health Monitoring
Ongoing monitoring of patient health conditions is crucial for early intervention and predicting complications. AI-driven solutions analyze real-time health indicators and identify deviations. This data allows medical professionals to act quickly in emergencies and prevent severe outcomes.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems are a typical example of AI-based patient health monitoring. These small and convenient wearable devices monitor blood glucose levels remotely. The tool collects and analyzes data to predict trends and offer personalized recommendations. It also forwards the information to healthcare providers to keep them updated.
Improving Gene Editing
AI implementation greatly benefits gene editing technologies and makes treatments more precise and effective. AI algorithms can analyze genetic data to identify potential targets for gene therapies. Think about the gene-editing technique CRISPR-Cas9. It uses AI to predict off-target effects, improve on-target efficiency, learn from experimental data, automate data analysis, and discover new gene editing techniques.
The Potential for AI to Reduce Healthcare Costs
Given the tangible benefits of the listed use cases, applying AI and ML to the healthcare sector has the potential to significantly lower costs for all stakeholders.
Hospitals that adopt AI and ML applications for data analysis and personnel management can more efficiently care for patients. Such software also reduces the number of costly errors and ineffective treatment decisions. Besides, it brings automation and improves staff management, preventing burnout and reducing staff retention and rehiring costs.
From the patient’s perspective, cost efficiency comes from improved service and better claim management. Chatbots and AI-driven applications help manage health conditions, transmit data to healthcare providers, and send alerts about possible complications. They also handle simple questions and queries. This way, patients don’t have to spend money on frequent hospital visits for minor health issues or chronic illness management.
In addition, AI enables insurance companies to automate claim processing and detect fraudulent transactions by identifying patterns people cannot spot. The risk of costly errors decreases significantly, and billing processes become automated.
Top Examples of AI Applications in Healthcare
It is time to move to the best real-world examples of AI algorithms’ application in healthcare. We have mentioned some of them before, but they all deserve more precise attention. The following examples of AI applications in medicine demonstrate its capabilities, advantages, and potential limitations.

H2O.ai
H2O.ai is reshaping patient care, diagnostics, and treatments through AI. It analyzes health data, finds patterns, and predicts patient outcomes, helping doctors create treatment plans tailored to each patient’s unique genetics, medical history, and daily habits for more personalized care. H2O.ai also streamlines hospital operations, making the healthcare system more efficient.
Working with the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), H2O.ai has created AI algorithms to process the 1.4 million faxed patient referrals and other documents UCSF’s health system receives yearly. The solution spots groups and ranks document types, pulling out key patient data to help staff and eliminate manual data entry.
H2O.ai has also recently announced the release of an open-weight small language model. The H2O-Danube3 series is suitable for devices with limited resources and works efficiently on consumer-grade hardware. It means more innovations in smart wearables will be coming soon.
PathAI
PathAI is a global leader in AI-powered pathology that improves diagnostics and patient outcomes. As of today, they perform best in drug development for complex diseases.
PathExplore — the offspring of PathAI — offers exceptional tumor microenvironment (TME) resolution from H&E whole-slide images. It is currently available for the following types of cancer: breast, colorectal, gastric, non-small cell lung, pancreatic, prostate, renal cell carcinoma, and melanoma. More indications are set to launch later this year. On August 29, 2023, PathAI announced that it had been selected as a technology partner with FNIH, aiming to enhance mucosal healing research with AI-driven precision.
Viz.ai
Viz.ai was created as an AI-driven model for stroke diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. The foremost objective was to speed the treatment process and reduce the chances of adverse outcomes and disabilities. Afterward, it extended its focus to include pulmonary embolisms and aortic disease.
At the core of the Viz.ai system is an extensive library of scans. When a patient’s brain image is input into the system, the AI algorithm compares it with all the databases, identifies similarities and patterns, and provides insights. The goal is to detect early signs of strokes and alert doctors about them. Medical specialists can view these images on their AI-powered mobile apps within their healthcare profiles.
Moreover, Viz.ai enhances collaboration between different parts of the healthcare system. The platform synchronizes doctors’ profiles and other personnel involved in each case to ensure they receive timely updates. It improves coordination and helps distribute patients among medical experts.
FWA360Leads
Healthcare Fraud Shield (HCFS) offers automated solutions to fight health insurance fraud, waste, and abuse (FWA). Their platform uses unique data sources and smart algorithms to boost FWA detection. HCFS provides a Software-as-a-Service model to roll out improvements and analytics.
HCFS just released FWA360Leads, a new tool that uses AI and machine learning to spot and rank high-value FWA leads. This product works with HCFS’s current FWA Precision Engine™ platform. FWA360Leads helps health insurers find risky cases and gives valuable insights. Companies using this tool say it pays off well and saves time and money.
NDIVIA for Healthcare
NVIDIA is famous for its high-performance graphics processing units (GPUs). It has included AI in its software and now plays a significant role in many fields. For instance, NVIDIA’s solutions help improve patient care, speed up medical studies, and make healthcare smoother.
In 2024, NVIDIA rolled out 25 new microservices for the healthcare world. These services are part of the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software package and offer tools for medical imaging, understanding natural language, and discovering drugs. These new tools allow healthcare providers to use AI tech more efficiently, leading to quicker diagnoses and better patient treatment plans.
Conclusion
The benefits of AI application in healthcare are very broad, as well as the uses. You can power your medical systems with AI to track patient health, send real-time alerts to medical staff, perform robotic surgeries, and more. AI technologies simplify the lives of everyone engaged in the healthcare system. While patients get enhanced quality of care, medical teams get more powerful tools to diagnose, monitor, and treat people. AI optimizes many routine healthcare workflows, allowing doctors to focus on care instead of reading data and managing documents.
AI applications for healthcare are rapidly developing and are likely to change the nature and prospects of the industry. Their full potential is still debated, but its effects on healthcare efficiency are evident.