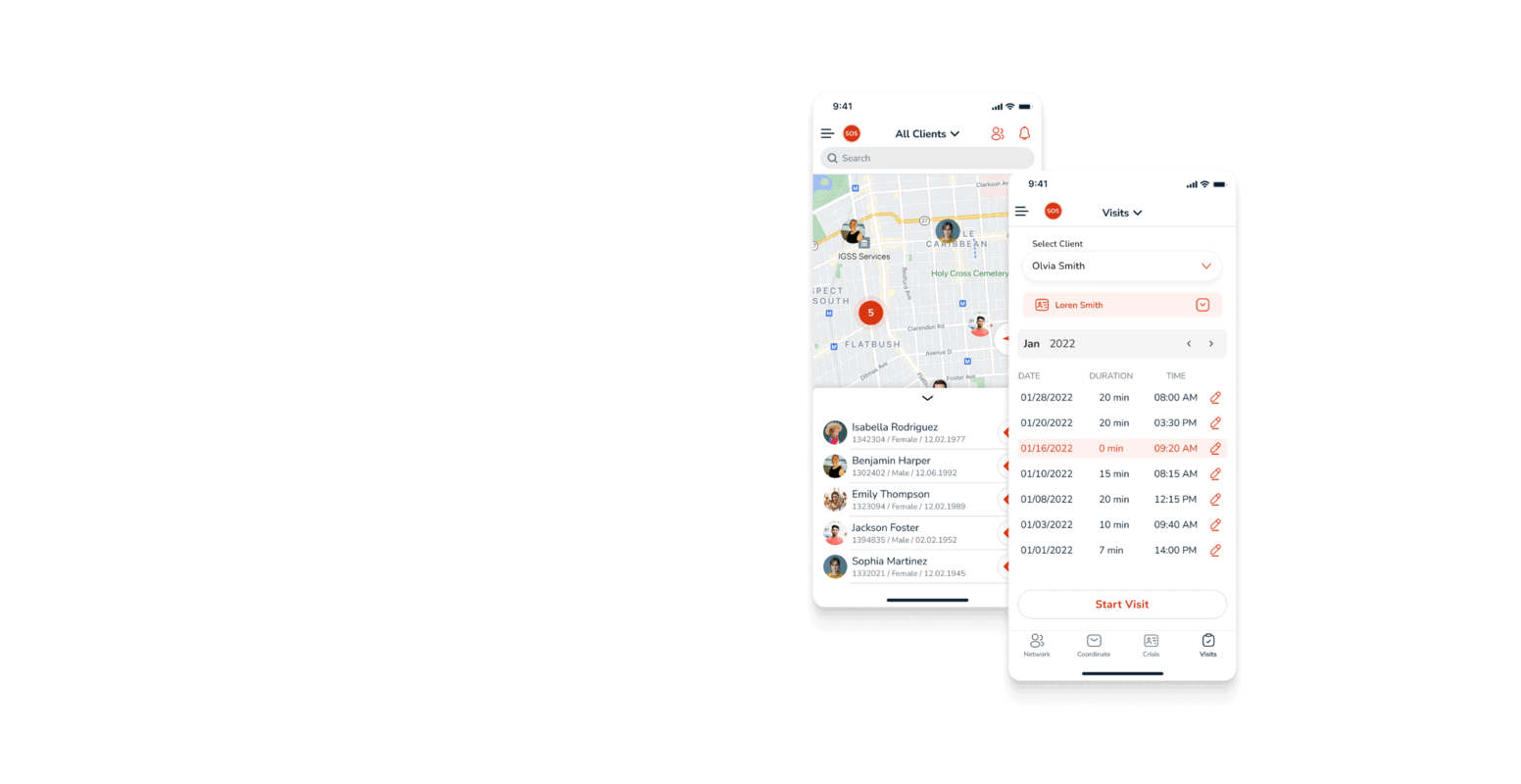
We often believe that more healthcare data means better outcomes. Yet, without the sophisticated analysis that healthcare data warehouse enable, are we simply swimming in a sea of data without direction? This question might make you pause and think. After all, in an age where we can track our every step, heartbeat, and calorie, it seems only natural that more data should lead to better health, right?
Wrong. Here’s the twist: having heaps of data is one thing; making sense of it is another beast entirely. Imagine a library. But instead of books, it’s filled with every piece of health data ever collected about you. From the flu, you had when you were five to the sprained ankle last summer. Now, what if someone could connect the dots between your sprained ankle and your flu to predict future health issues? That’s the magic of data warehousing in healthcare.
What Is A Healthcare Data Warehouse?
A healthcare data warehouse (HDW) is a centralized repository designed to store and manage vast amounts of health-related data collected from various sources. We’re talking about everything from patient records and lab results to insurance information and clinical studies.
First, consider the sources of healthcare data. These include hospitals, clinics, labs, and even wearable devices that track your steps and heart rate. Each of these generates a piece of the puzzle that is your health story. But when these pieces are scattered, it’s hard to see the full picture. This is where HDWs come into play.
Data warehouse in healthcare takes this jumble of information and sifts through it, highlighting patterns, trends, and warnings we’d otherwise miss. For instance, if data shows that patients with a certain condition tend to develop complications after a specific treatment, doctors can adjust their approaches to improve outcomes.
In a nutshell, HDWs are not just about storing data; they’re about using that data to transform healthcare. They turn information into insights, insights into action, and action into improved health outcomes. The importance of effective healthcare data management is highlighted by the projected growth of the data warehouse healthcare industry, which is expected to grow from US$3.9 billion in 2023 to an impressive US$12.49 billion by 2030.
Common Data Warehouse Models
Data warehouses stand as colossal libraries of information, serving as the backbone for decision-making across industries. Yet, not all of them are built the same. Let’s explore three key models: virtual warehouse, data mart, and enterprise data warehouse. Each plays a pivotal role in transforming raw data into actionable insights.
Virtual Warehouse
The virtual warehouse creates a dynamic view of data spread across different systems. This approach allows businesses to query data in real-time, directly from its source, offering up-to-the-minute insights without the need for extensive storage infrastructure. Companies are stuck in the data swamp, spending much more effort on collecting and cleaning data than on extracting insights. 42% of their time companies spend on data profiling and preparation, another 16% of their time on data quality monitoring, and only 12% of the time on analysis. With the help of virtual warehouse technology, a company might use it to provide real-time sales analytics by pulling data from various online and in-store sales systems. This immediate access to data makes the virtual warehouse ideal for scenarios where speed and flexibility are paramount.
Data Mart
Data mart offers a curated selection of data to meet the distinct needs of individual departments or teams. By providing a concentrated slice of the data warehouse tailored to specific requirements, data marts enable faster, more relevant data retrieval. A staggering 70% to 80% of corporate business intelligence initiatives fall short of their goals due to inadequate data handling and a frustrating user experience.
For example, a marketing team might use a data mart dedicated to customer behavior and campaign performance, streamlining their analysis and strategy development processes.
Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW)
An enterprise data warehouse (EDW) is designed to consolidate and store all of an organization’s data in one massive repository. It’s the central hub from which all data analysis, reporting, and business intelligence activities are conducted. EDWs support complex queries and large-scale data integration, making them ideal for organizations looking to derive strategic insights from vast amounts of data across various departments. An EDW could, for instance, enable a multinational corporation to integrate and analyze data from all its global operations, identifying efficiencies, trends, and opportunities for growth.
Each of these data warehouse models serves a unique purpose. The agile virtual warehouse facilitates real-time data access, and data marts offer department-specific insights. Enterprise data warehouse, in turn, enables a bird’s-eye view of an organization’s data landscape.
This is just a brief description of complex solutions. Having an in-depth understanding of these data models is key to leveraging the right data strategies for your organization’s needs. This ensures you’re not just collecting data, but also turning it into a strategic asset.
Benefits Of Healthcare Data Warehousing
Data warehouse in healthcare offers an array of benefits that streamline operations, enhance patient care, and improve financial performance. It centralizes health-related data and provides a powerful tool for analysis, decision-making, and strategy development. Let’s explore the key advantages it brings to the healthcare sector.
Out-of-the-Box Reporting
The process of generating reports can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours. Data warehouses significantly enhance organizational efficiency and reduce the time of creating such reports by enabling the swift generation of detailed out-of-the-box reports. For example, a hospital might use this feature to track the success rates of surgeries across different demographics. It facilitates rapid adjustments to improve care.
A key issue addressed by data warehouses is the elimination of data silos, a common obstacle where disjointed data systems lead to inconsistent and inaccessible data across departments. Data warehouse solutions consolidate data into a single, coherent system. It results in a unified data view that supports informed decision-making and analysis based on a comprehensive dataset.
Reduce Redundant Tests or Procedures
Data warehousing solutions make a significant contribution to healthcare efficiency by identifying patterns of repeated tests or procedures that could be omitted. This results in significant cost savings. Through comprehensive analysis, this technology helps to identify that certain routine checks are being performed more frequently than required. This insight is especially relevant given that approximately 30% of laboratory tests are considered unnecessary. The data repository enables critical reflection on existing protocols and facilitates changes to guidelines. This, in turn, helps reduce the number of unnecessary tests for patients and provides a more targeted and patient-centric approach to healthcare.
Improve Supply Chain Management
Overstocking and understocking are common problems in medical facilities, impacting the efficiency of healthcare delivery. Hospitals in the United States incur around $25.4 billion in needless supply chain-related expenses on an annual basis.
These issues arise due to various factors including, but not limited to:
- inaccurate demand forecasting,
- inefficient inventory management practices,
- the unpredictable nature of healthcare needs, especially in emergency situations or during public health crises like pandemics.
Leading healthcare providers are making concerted efforts to scrutinize and account for their waste more precisely – some even subdividing their waste types into 37 separate classifications, in a bid to integrate superior sustainability and cost optimization into their workflows.
Data warehouse technology plays a vital role in predicting demand for medical supplies and medications. It helps to analyze usage patterns and inventory levels, so hospitals can optimize orders, reduce waste, and ensure that critical supplies are always available without overstocking.
Informed Treatment Decisions
Healthcare data warehouses aggregate vast amounts of patient data that enable doctors to make more informed treatment decisions. This could include leveraging historical data to predict individual patient responses to specific treatments, thus personalizing care plans to increase effectiveness and reduce side effects.This is especially important, as reducing side effects enhances patient safety and ensures treatments are both effective and tolerable, leading to better adherence to treatment plans. A worldwide analysis suggests non-adherence to medication regimens could be linked to annual healthcare costs exceeding $52,000 per person. One of the leading causes of non-compliance with medication is the worry about experiencing unwanted effects. Side effects are a widespread issue and are a common cause of hospital admissions.
Population Health Management
Population Health Management systems, which were valued at approximately $31 billion in 2023 and are anticipated to surpass $157.87 billion by 2033, play a crucial role in leveraging data to oversee and enhance health outcomes across vast populations. In response to the escalating costs of healthcare and the growing epidemic of chronic diseases in the U.S., policymakers are increasingly adopting value-based payment models that aim to achieve a dual benefit: reducing expenditures while optimizing patient outcomes. Despite advancements in diabetes treatment and prevention, the burden of the disease in the USA remains significant. More than 34 million people have diabetes, and these patients account for a quarter of all healthcare spending.
Data warehouse systems are built to manage and analyze data to pinpoint health trends, risk factors, and potential preventive measures. For instance, the analysis of regional data might uncover an increase in diabetes cases, prompting targeted preventive campaigns and interventions.
Integrated Data Repository
Integrated data repositories have emerged as a critical solution to the widespread problem of patient information fragmentation in healthcare, a problem that makes effective and accurate patient care significantly more difficult. By centralizing detailed patient histories, test results, and other important information into healthcare data warehouses, these repositories ensure that all important data is stored in one, easily accessible place. This allows healthcare providers to quickly access important information, leading to faster and more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Key Features To Look For In Healthcare Data Warehouse
Building an efficient and effective HDW involves more than just aggregating huge volumes of data. This requires a strategic approach to design and functionality that focuses on the specific needs of healthcare analytics, patient care optimization, and operational efficiency. Here are the key features to look for in HDWs to ensure they meet the complex demands of the healthcare industry.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
EDI allows the seamless exchange of data between different healthcare systems and streamlines processes like billing, patient records management, and supply chain operations. For example, a hospital can use EDI to automatically send patient information to an insurance company for faster billing and claim processing.
Single Sign-On (SSO)
SSO offers users access to multiple applications with a single set of credentials, makes much easier the login process, and enhances user experience. In a healthcare setting, this means that physicians can quickly access patient records, lab results, and other applications without repeatedly logging in, saving time and reducing frustration.
Your next read: Case Study – Lab Testing Platform: A Comprehensive Cloud Portal for Managing, Tracking, And Accessing Drug Testing Data
Data Integration and Interoperability
The sheer volume and complexity of healthcare data, including unstructured data from notes and structured data from medical records, pose significant challenges. Managing this vast amount of information, which accounts for approximately 30% of the world’s data volume, requires advanced storage solutions and data management strategies to ensure that healthcare providers can access and analyze the information efficiently.
Lack of interoperability leads to delays in care, increased medical errors, and increased costs, and hinders innovation in digital health. Given the urgency of addressing these challenges, the global healthcare interoperability solutions market is expected to grow by $3330.16 million from 2022 to 2027, highlighting the urgent need for technologies that enable efficient sharing and use of data.
A healthcare data warehouse (HDW) that integrates data from disparate sources, including data lakes, machine learning software, and self-service business intelligence tools, solves this problem by providing a single view of information. This integration is not just about data centralization; It’s about being able to provide comprehensive analysis and insights that can significantly improve patient care and healthcare operations. For example, by integrating wearable device data with traditional medical records, healthcare providers can gain greater insight into patients’ health status, leading to personalized treatment plans, proactive health management, and improved health outcomes.
Security and Compliance
Given the sensitivity of health information, security and compliance with regulations like HIPAA are non-negotiable. From 2009 to 2023, the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) received reports of 5,887 data breaches in the healthcare sector, each involving 500 or more records, underscoring the critical need for robust security measures. Interestingly, the most common reason for these breaches was unauthorized access or disclosure, demonstrating the vulnerability of health information to both external and internal threats.
Healthcare data has a long lifecycle, often needing to be preserved for decades, which increases the complexity of safeguarding it against evolving cybersecurity threats over time. To address these challenges, healthcare organizations deploy advanced security measures that includes encryption to protect data at rest and in transit, comprehensive access control systems to ensure only authorized personnel can access sensitive information, and regular security audits to identify and rectify potential vulnerabilities.
Data Storage Scalability
Healthcare organizations are experiencing an exponential increase in data volume due to the digitization of health records, diagnostic imaging, and the rise of wearable technology. The challenge lies in guaranteeing that data storage solutions can scale to meet these growing demands without compromising performance or reliability. For instance, a hospital must be able to expand its data storage capacity quickly and efficiently as its data grows.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
The critical nature of healthcare information necessitates robust data backup and disaster recovery plans. Healthcare providers need to ensure that patient data is not only backed up but also can be quickly recovered after any data loss event, whether it’s due to a cyberattack, natural disaster, or system failure. This is underscored by the fact that 93% of businesses that experienced a data loss for more than 10 days went bankrupt within a year following the incident, and half of those filed for bankruptcy right away.
The realm of healthcare data is multifaceted. It ranges from individual pieces of patient information to the massive waves of insights generated by big data analytics. It makes the task of managing this critical information quite complex. Healthcare providers face unique hurdles as they attempt to navigate through this extensive pool of data. As the industry continues to digitize patient records, implement electronic health records (EHRs), and use various health informatics systems, the importance of effective data storage solutions has never been more apparent.
As you can see, each of these features enables healthcare organizations to manage, analyze, and secure vast amounts of data, turning it into a powerful tool that boosts patient care and operational efficiency.
Healthcare Data Warehouse Investments
Investing in a healthcare data warehouse (HDW) is an important decision for healthcare organizations that promises significant returns in terms of improved patient care, operational efficiency, and strategic insight. HDW implementation costs can vary widely, typically ranging from $70,000 to over $1,000,000. This option largely depends on the size of the project, including factors such as the number of data sources to integrate, the complexity and volume of the data, and specific security requirements. For example, integrating data from multiple systems such as ERP, EHR/EMR, CRM, and pharmacy management systems, each with its own structure and data format, can have a significant impact on project costs.
Moreover, the size of the healthcare organization is an important aspect to consider when determining the size of the investment. Small companies with 200 to 500 employees may face costs ranging from $70,000 to $200,000, while larger organizations with more than 1,000 employees may require an investment of $400,000 to $1,000,000 USA. These figures highlight the importance of careful planning and consideration of key cost factors such as data inconsistency, the volume of data processed, and performance requirements such as speed, scalability, and fault tolerance.
A Path To Implementing A Healthcare Data Warehouse
The move to implement a health data warehouse (HDW) is a strategic step toward leveraging data to improve healthcare outcomes. This journey involves several clearly defined steps, each of which is critical to the successful integration and use of a healthcare data warehouse. Here’s how to manage this transformative process.
| Healthcare Data Discovery | The first step is data discovery, where you identify and understand the sources and types of healthcare data available. This includes data from electronic health records (EHRs), lab systems, patient feedback, and more. In order to shape the scope of your HDW it is essential to understand the landscape of your data. |
| Planning | This phase involves defining the objectives, scope, and expected outcomes of your HDW. It also includes assessing the technological requirements and assembling a skilled team to bring your vision to life. |
| Design | Designing your HDW involves creating a blueprint that outlines how data will be stored, processed, and accessed. The goal of this phase is to make sure that the architecture of the HDW meets the specific needs of healthcare providers, patients, and administrators, facilitating efficient data management and analysis. |
| Development | With a design in place, the development phase brings the HDW to life. This involves building the data warehouse structure, integrating data sources, and developing the necessary tools for data analysis and reporting. The development phase is where technical expertise is vital to transform plans and designs into a functional HDW. |
| Testing | Testing is critical to ensure the HDW operates as intended. This includes verifying data integrity, performance testing under various loads, and security testing to protect sensitive information. Post-migration testing ensures that data has been accurately transferred from legacy systems to the new HDW without loss or corruption. |
| Deployment | The final step is deploying the HDW within the healthcare organization. This involves making the HDW accessible to users, providing training as necessary, and beginning the process of using the warehouse to achieve improved healthcare outcomes. |
A healthcare data warehouse implementation is a significant undertaking. The result is a powerful tool that leverages the full potential of healthcare data to improve patient care, enhance operational efficiency, and inform strategic decisions.
Healthcare Data Warehouse Use Cases
As you can see, data warehouses have become indispensable tools that drive innovation and improve patient care across multiple domains. By centralizing and harmonizing vast amounts of data, HDWs offer unprecedented opportunities for analysis, insight, and action. Let’s delve into how HDWs are used in various areas of healthcare.
Patient Records Management
HDWs streamline patient records management by providing a comprehensive, unified view of patient data. For example, the Epic Systems software, widely used in hospitals, functions as an HDW by consolidating patient records across departments, ensuring that healthcare providers have immediate access to a patient’s complete medical history, from laboratory results and imaging scans to previous treatments and ongoing care plans. Similarly, Cerner’s Health Information System provides another robust example, enabling the seamless integration of data from different healthcare settings, thereby facilitating a comprehensive view of patient data. This holistic view supports more informed decision-making and personalized patient care.
Health Data Analytics
In the domain of health data analytics, HDWs are powerful allies. They enable healthcare organizations to analyze patterns and trends across large datasets, identifying potential health risks and outcomes. A real-world example of this application can be seen in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which uses HDW to track and manage infectious disease outbreaks. Using the Health Data Warehouse (HDW), the CDC analyzes data from various sources, including hospitals, laboratories, and public health departments. This analysis helps to monitor the spread of diseases such as influenza or COVID-19. Additionally, it assesses the impact of vaccinations and other public health measures and makes forecasts based on the gathered data.
This data-driven approach allows the CDC and similar public health organizations to develop informed and proactive responses to public health issues. It illustrates the critical role of the Health Data Warehouse (HDW) in promoting the effective analysis of health data for broader public benefit.
Learn more about data analytics usage in our blog post: Personalized Medicine and Beyond: Data Science for a Healthier Future
Clinical Trials
Clinical Trials are a major investment area for US pharmaceutical companies, accounting for nearly 40% of their research budget and totaling around $7 billion per year. HDWs significantly contribute to the efficiency of these trials. A notable example of this is how Pfizer utilized HDWs during the development of their COVID-19 vaccine. By integrating and analyzing clinical data from diverse sources, including patient records, lab results, and observations made during the trials, HDWs enabled Pfizer’s researchers to swiftly identify patterns and responses to the vaccine
This comprehensive data analysis through HDWs sped up the pace of the trials as well as bolstered the reliability of the outcomes, facilitating rapid progress toward innovative medical treatments. Such applications of HDWs in clinical trials underscore their vital contribution to advancing medical research and treatment breakthroughs.
Telemedicine
In the telemedicine space, HDWs facilitate remote patient monitoring and care by aggregating data from wearable devices, electronic health records, and telemedicine platforms. A practical example of this can be seen with the telehealth services provided by Teladoc Health, which uses HDWs to offer comprehensive remote patient care. Teladoc integrates data from patients’ wearable devices that track vital signs, along with their medical histories via telemedicine platforms. As a result, Teladoc Health professionals could make real-time decisions about patient care. This approach is especially effective when monitoring patients with chronic diseases and allows treatment plans to be adjusted based on up-to-date data analysis.
Healthcare Data Warehouse: Bottomline
To summarize, the advent of health data warehousing represents a monumental shift towards data-driven healthcare decision-making. These robust systems enable healthcare providers to make informed decisions based on accurate and consolidated data from multiple sources. The benefits of implementing a health data warehouse are vast and varied, from improving patient care by analyzing disease patterns and treatment outcomes to streamlining administrative operations by identifying inefficiencies and fraud. Moreover, these systems pave the way for groundbreaking research and innovation, offering new insights into disease prevention and treatment strategies.
As healthcare continues to evolve, the importance of an optimized data analytics approach cannot be overstated. Empeek is at the forefront of this digital health revolution and provides expertise and innovative solutions that enable healthcare organizations to harness the full potential of their data. By providing the tools and support needed to implement a sophisticated healthcare data warehouse, our team enables healthcare to stay ahead in the rapidly changing healthcare landscape.