Seeing through skin and tissue, creating one’s reality on the street, being able to do micro-invasive operations with the help of special glasses that allow re-creating the 3D models of the internals… No, that’s not a new sci-fi movie script – it’s a reality that the healthcare industry is beginning to explore and benefit daily. Virtual reality and augmented reality in healthcare have been titled as the future of medicine since it entered the market – and there are plenty of reasons to prove this argument.
In this article, we’ll explain what augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies mean for the healthcare industry, how doctors can use virtual reality in medicine and surgery, what are most popular medical VR apps and AR solutions on the market, the benefits of implementation of AR and VR in healthcare, and how to estimate the cost of medical AR software.
VR and AR in Healthcare: What It Is and How It Works
Shortly put, augmented and virtual reality technologies help healthcare providers to achieve either immediate goals (for curing or treatment) or long-term ones (when used for teaching/learning purposes). Sometimes, the names of these two different technologies are used interchangeably, though there is a difference between them we’ll cover in a bit. Let’s have a look at what AR/VR technologies are made of first.
Components of AR/VR Technologies
Any virtual or augmented reality should have both hardware components to interact with the reality and software to process, analyze, interpret, and construct the needed ‘extra’. The below is the list of commonly used hard- and software components.
AR/VR hardware includes:
- Sensors/tracking devices: digital cameras, optical sensors, accelerometers, GPS, gyroscopes, solid-state compasses, RFID, and wireless sensors);
- User’s input devices: microphones, touch screens, gesture devices, stylus, pointers, gloves, or other body wear;
- CPU and display/output devices: smart glasses, lenses, laptops, smartphones, and tablets.
AR/VR software includes:
- Applications and programs that receive and interpret the data transmitted from/to the hardware/wearables to create an additional or simulated reality.
What Is the Difference Between Medical AR and VR
While AR in healthcare uses cameras, displays, and sensors to overlay onto the arrangement of things in the real world, the VR in healthcare constructs the whole world based on the parameters and inputs you provide or based on those automatically provided by the database. For instance, while AR technology provides the holographic projection of the particular organ in the real world, VR tools allow us to immerse into a simulated body and ‘navigate’ inside.
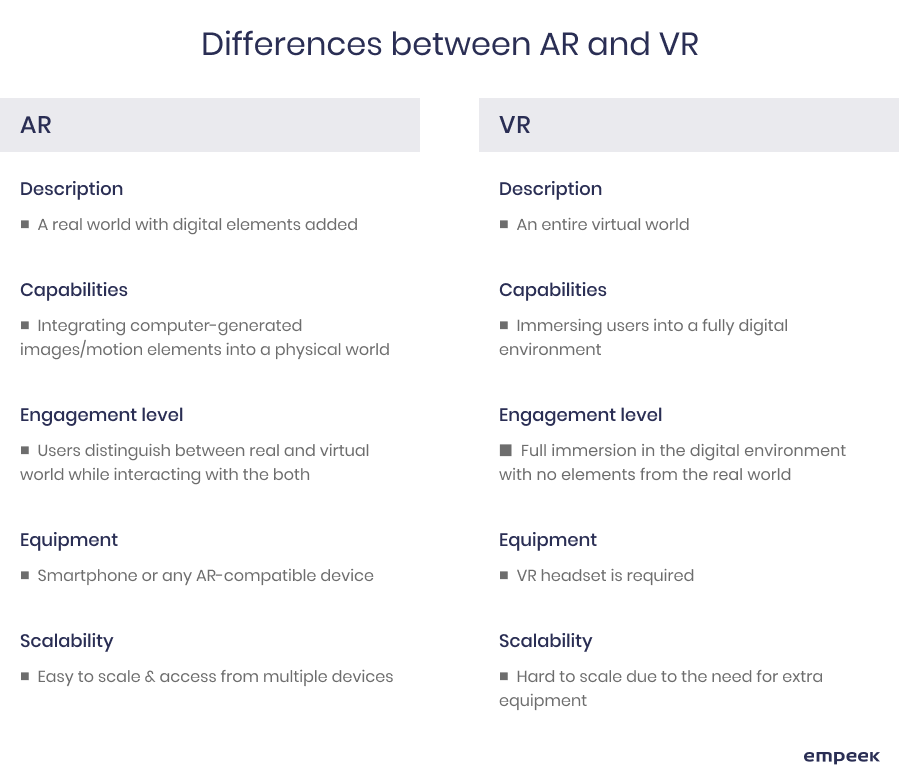
Knowing the difference between AR and VR solutions is crucial for understanding where each of these virtual care technologies can be applied to achieve specific goals. Let’s view a few examples.
Insight on Augmented Reality in Medicine
The most common example when it comes to its practical application will be the 3D-visualization of the patient’s body for the surgeon during the operation. It’s not a novel concept by far as the talks around using the AR programs and machine learning for surgeons have been held since 2015. Yet, in 2019, there was the first surgical procedure carried out utilizing the ARAI system. At the end of 2020, the surgeons from the Balgrist University Hospital performed the first holographically navigated spine surgery using the HoloLens 2. In that case, the surgeon had a 3D representation of the affected anatomy generated and projected into the surgical field thus overlaying the anatomy of the patient during the operation. Some may call it magic, we call it a very creatable and effective addition to reality.
Insight on Virtual Reality in Medicine
VR has been in healthcare since 1990 and it only developed the quality and ability of the doctors to recreate more realistic images based on the CT and MRI scans and x-Ray images. For instance, with the use of virtual reality applications in healthcare, doctors can create the model of the affected organ, tissue, or joint and understand the possible pitfalls that future surgery can have. Just like it happened in 2017 during the surgical separation of conjoined twins. Thanks to the VR and 3D models based on the images, the surgeons were able to see the ‘bridge’ between the twins’ hearts before the operation so they could adjust their plan for surgery. Without it, they would’ve been able to notice it only during the operation.
Of course, these are just a few examples of successful adoption of AR technology in healthcare. Let’s see what the future holds for it in the future and what the market prognosis is.
AR and Virtual Reality in Healthcare: Current State and Future Perspective
Both AR and VR medical applications are utilized in practice to achieve the treatment goals, improve patient outcomes, enhance the patient’s understanding of the medical processes, and teach the new generation of doctors. There are multiple areas in health care where AR/VR technology can be applied successfully. Let’s explore them below.
The use of augmented reality medical applications includes but is not limited to the following practices:
- Surgical treatment: 3D visualization of the internal organs that are about to be operated on to avoid extra incisions, creating the 3D models of the operated organ to plan the surgery, allowing the surgeons to ‘see through the tissue’ of the patients;
- Accurate diagnostics: using AR/VR tools to help patients better describe what bothers them, which increases the chance of being diagnosed correctly;
- Closest-to-real situation lab practice: providing hands-on experience for medical students so they can visualize their action’s impact on the human body;
- AR-based navigation: indicating the medical tools like defibrillators, emergency kits, nearest medical facilities, navigating the hospital;
- Virtual assistance during an emergency enabling the effective collaboration between the first point emergency contact and a doctor distantly;
- Patient-physician interaction in cases where the physical contact should be limited (due to pandemic, location, etc);
- Anatomy teaching at schools: the kids will better understand their bodies when they can immerse into the learning process;
- Pharmaceutic visualization of the drug’s pharmacodynamics/pharmacokinetics, etc.
Some of these practices are already widely used in the medical field, especially surgery and medical studies while others are expected to be incorporated into doctor’s medical workflow in the nearest future. Why do we think that way? There are plenty of market indicators that explain it.
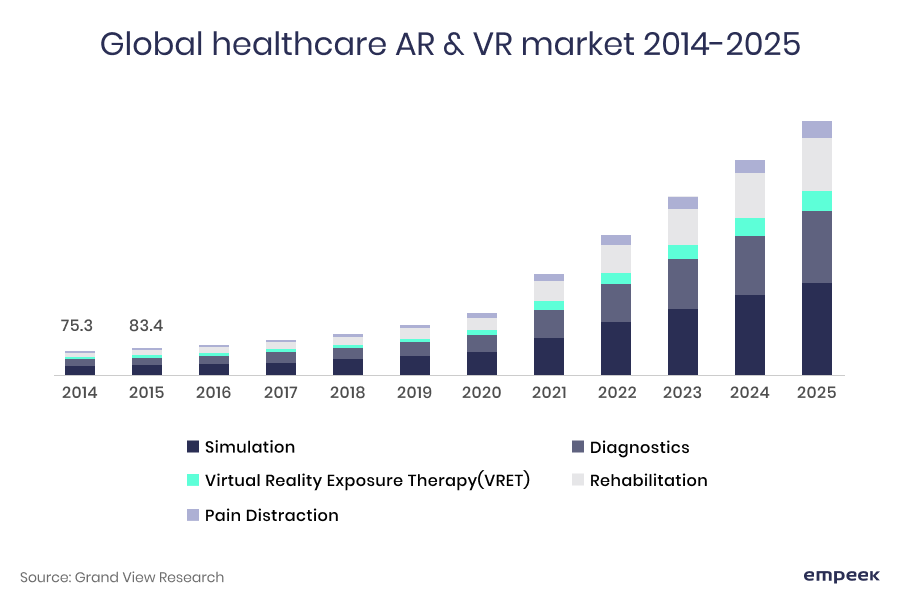
Market Reality of VR and AR in the Healthcare Sector
As the most recent statistic shows, the number of investments and market share of the AR and VR industry is expected to increase by 8-10 times depending on the region. The North American market, valued at $477m in 2018, will become $4.64 bn by 2025. And no wonder, since the use of virtual reality in medical field will include physician training, treatment, and hospital management.
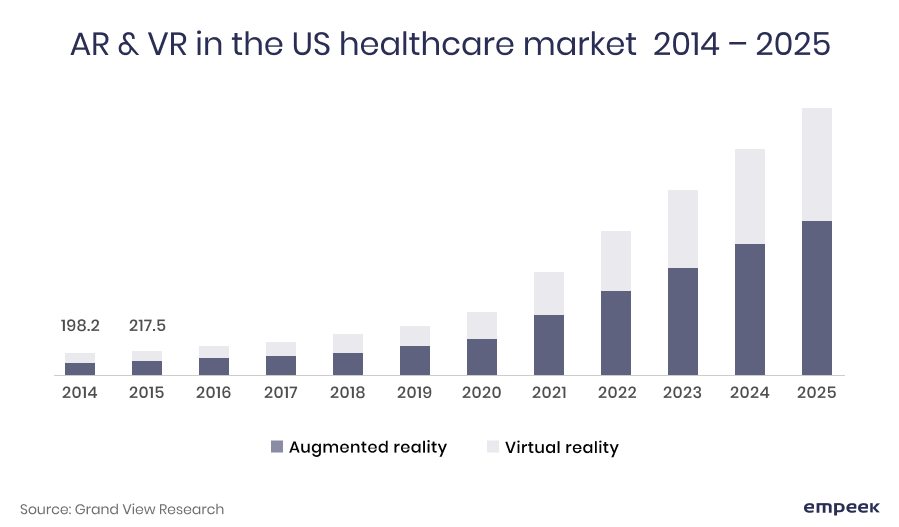
Regarding the segmentation of AR and VR, the market is primarily divided into the following categories based on the level of interaction with reality and the tools used:
- Mobile AR platform
- Monocular AR
- Binocular AR
- Full Immersive VR
- Semi-Immersive VR
- Non- Immersive VR
Each of these segments is predicted to expand on both a local and international scale in the next couple of years as a result of technological advancements and the benefits their implementation has to the healthcare system. There are already the key players on the market like Oculus VR, Google, Microsoft, 3D System Inc., Hologic Inc, and others that push the advancements forward. So, why don’t cover what is already done so far by showing the best examples of augmented and virtual reality in healthcare?
Best Examples of Virtual and Augmented Reality in Medicine
The AR and VR equipment and software are used in various fields of medicine – from dentistry to surgery to clinical imaging and so on. Below is the list of the best applications that have already proven their efficacy in practice.
AED4EU

For people with certain medical conditions, the matter of time is a matter of survival and in emergencies, they’re dependent on how fast the passers-by will respond. With the AED4EU application available via Layar Reality Browser, the users can quickly detect the location of the closest automated external defibrillators (AEDs). This can save the lives of those who have a sudden cardiac arrest in public space.
AccuVein
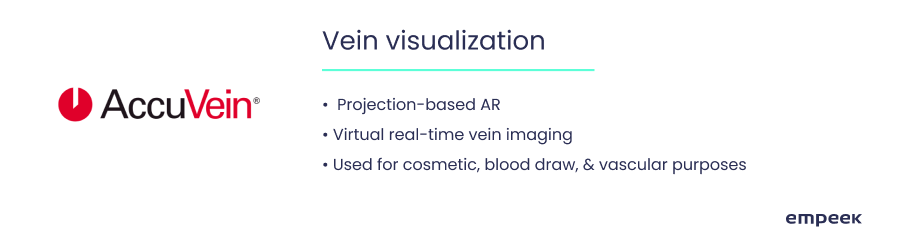
No more blind injections, stress, and hematomas caused by injections! With AccuVein, the nurses can see ‘through’ the patient’s tissue by using the handheld scanner. This is a great solution that benefits both sides: physicians and nurses save time on injecting the medicine while the patient experiences less stress during the procedures. AccuVein is mostly used for children and the elder.
HoloAnatomy

Learning about the human body has never been more interesting, immersive, and digital than it is now with the HoloAnatomy. Paired with Microsoft’s HoloLens, this application creates a mixed reality for the students so they can study human anatomy with a high level of detail. Plus, their practice won’t be limited by the availability of cadavers for dissections as they can ‘dissect’ the virtual organs, see the interaction between the different body systems, and view every part under every angle. This will influence the quality of learning and will prepare a better-trained generation of doctors.
Virtuali-tee T-shirt
Virtuali-tee is another great invention for teaching human anatomy to kids in a highly interactive way. You can see the parts of human bodies as holograms when you scan a QR-code on the T-shirt. These codes are located in the same places where the real organs are, so when you scan the code in the heart area, you can see the human heart in detail.
AIRA Smart Glasses

This is the project which is aimed at helping visually impaired people to get as much information about the outer world as needed to move safely and become more active. AIRA smart specs are special glasses that use a lot of sensors and tracking tools that interpret the outer visual information into audio. In this way, legally blind people will have more input about their surroundings and they can have more independence when it comes to household activities or walking around.
As you see, the examples are plenty, and this list can go on and on. If you’re a healthcare provider that wants to make sure your clients get best-in-class treatment and care, you definitely should consider implementing medical augmented reality solutions into the practice. And you may wonder how much it can cost. Well, this is what our next part is about.
AR in the Healthcare Sector: How to Calculate the App Cost
You probably anticipate seeing the exact figure here and we have to disappoint you right away: no reputable agency can give you the precise price even after you’ve explained what you want to get in the end. The thing is, for the VR/AR product to really make a positive impact, the developers have to go through the discovery stage first. That includes gathering all the necessary input information from you, doing business analysis, planning the UX/IU design and architecture, etc.
Yet, these aren’t the only factors that influence the development cost. What else does?
- Type of AR app: market-based, location-based, visual odometry-based
- Type of software development kit (SDK) and supported platforms
- Type of maturity (minimum viable product or ready-to-market)
- Number of features it will have
- Linking the new VR/AR into your existing system
- Number of test projects
- AI/ML implementation
- Use of the hardware and related expenses
- Use of the technologies and solutions that will comply with the local laws and regulations.
While these are the major factors that will add up to the cost of the AR/VR app, though the final estimate will depend on your end goals. Don’t hesitate to reach out and ask how we can help you create the augmented reality app for you to enhance the quality of care you provide.
Final Thoughts
Virtual and augmented reality in medical field is becoming more widespread and common in daily healthcare practice. Their use allows the doctors to provide more effective, less invasive, and overall better care to their patients while for the medical students, it offers more hands-on experience during learning.
With the increased demand for AR/VR medical technologies and their proven efficacy, many healthcare providers are ready to implement them in their daily practices to make their patients’ experience better. At Empeek, we are ready to add value to your business by creating AR software aimed at improving the doctors’ performance and patients’ outcomes. Contact us to discuss your project idea.








