In today’s world, healthcare is not limited to hospitals and clinics. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) companies harness the potential of advanced remote monitoring devices and software and bring it to patients’ homes. With its ability to provide real-time data, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the efficiency of healthcare delivery, RPM is in high demand. Approximately 70.6 million patients in the US will use RPM tools in 2025. Moreover, the growth in RPM market is expected to increase till 20.1% annually and reach $41.7 billion by 2028.
What is remote monitoring? How is the RPM development process going? This article will walk you through the primary information on RPMs based on Empeek’s years of experience in the healthcare industry.
Components of an RPM Solution as a Remote Monitoring System
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is a groundbreaking telemedicine technique that allows healthcare providers to monitor their patients’ physical data from a distance and respond to errors when they arise. Specifically used in chronic disease management, it can also apply during temporary conditions such as pregnancy, to ensure timely response. However, an efficient RPM cannot stand alone; it is a multi-component solution that demands extensive infrastructure. For this reason, this system must be compatible with existing health care systems and promote effective cross-communication. This article highlights some main components needed for successfully implementing and running an RPM system.
Remote Patient Monitoring Equipment
RPM devices are designed to gather essential patient health information, such as heart rate, blood glucose levels, and oxygen saturation. Health monitoring devices have sensors, such as wearables and implants, that continuously monitor and record patients’ physiological parameters and collect and transmit data such as heart rate, blood glucose level or blood pressure connect wirelessly to the center platform. This centralized system collects and analyzes data. As a result, healthcare providers can monitor patient health in real-time and thereby make informed decisions based on the collected information from home health monitors.
Apps for Patients
Patient software powers Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) systems. It delivers health data, medical insights, and key alerts. This app doesn’t gather data from medical devices monitors. Instead, it showcases information processed by other systems. Bluetooth tech links the app with various medical devices. This ensures your health data flows accurately.
Quite often, the software features communication tools. Patients can chat with doctors, complete health forms, and engage with their care team. It’s like having a digital health ally.
Healthcare Providers App
This specialized type of apps empowers healthcare specialists to manage their patients more efficiently. It offers doctors real-time access to patient data and allows them to:
- Monitor vital signs as they happen
- Review medical histories
- Receive instant alerts for any concerning changes
As a result, medical professionals can make well-informed decisions. With these types of apps, healthcare providers can stay one step ahead in patient care.
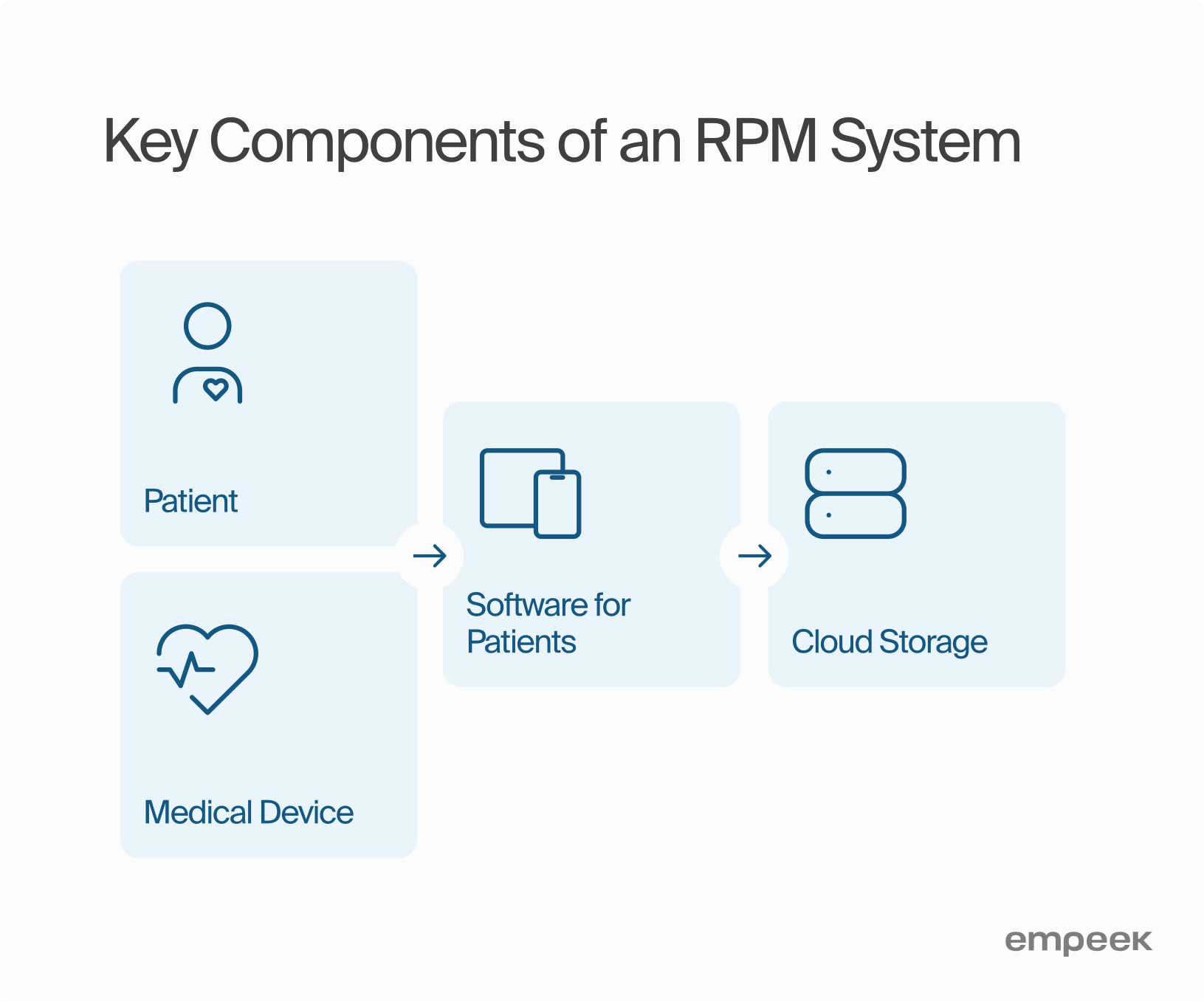
Data Storage
RPM systems must capture, sort, and secure patient data. They gather information from devices that vigilantly monitor patients. Most doctors—three out of four—now store this data in the cloud, since cloud storage holds ten times more data and rarely fails (IBM Cloud Services).
Effective storage revolutionizes practice. It allows doctors to review up to 1,000 data points per patient each day. Today, 89% of these systems integrate with other health tech tools. This collaboration reveals a clearer health picture. It boosts diagnostic accuracy by 40% and saves doctors three hours per patient each week.
Do you need help integrating your RPM system with these or other platforms? We offer expert support. Learn more about our integration services here.
Roadmap for Developing an Innovative Health Monitoring RPM Solution
Creating a remote patient monitoring app requires precise planning and deep understanding. Develop a strategy that incorporates best practices to refine the development and ensure robust security. With a well-structured roadmap, healthcare providers can build an RPM solution that enhances returns and drives meaningful change. To achieve this, assemble a skilled engineering team to execute your vision. Partnering with experts like Empeek often yields superior results. Navigate through essential phases of development, working closely to refine each step.
Here’s an in-depth guide to creating a remote monitoring system.
Step 1: Figure Out What You Need
To pick the right RPM, grasp your needs first. A tiny clinic might thrive with a basic RPM system. Such a system tracks essentials: heart rate, blood pressure. For example, in rural spots, 75% of doctors embrace remote monitoring for chronic care.
Yet, for complex cases like diabetes or heart disease, consider a tailored RPM. Opt for core features like continuous glucose checks or real-time alerts.
Health Recovery Solutions (HRS), hailed as “Best in KLAS” for RPM, suggests starting with a pilot program. Test RPM’s worth with patients and providers. Measure key metrics. Then tweak the system to boost impact and efficiency.
What to consider:
- Who will use the app? (e.g., elderly, people with chronic diseases)
- What health conditions will it monitor? (e.g., heart rate, blood pressure)
- How will it collect data? (e.g., wearable devices, sensors)
- Will it need to work with other systems? (e.g., electronic health records)
A thorough market analysis of existing off-the-shelf solutions is crucial in this process. By analyzing their strengths, weaknesses, and customer reviews, you can identify pitfalls and gain insights that will define the core values of your future RPM product. This analysis will also help determine the necessary functionalities for effective care delivery. Whether you aim to streamline your clinic’s operations or provide a solution to a broader audience of healthcare providers, this understanding will enable you to create a unique value proposition.
Step 2: Identify Target Users of the RPM Solution and Their Needs
In custom RPM app development, the next step is grasping user needs. This insight fuels the creation of features that let users efficiently track and manage health data.
Focus on these essentials: intuitive interfaces, vivid data visuals, real-time alerts for emergencies, and smooth integration with current systems.
Now, we can tailor the app to diverse patient groups and adapt to various needs, like simple data inputs or voice commands. This will boost engagement and encourage proactive health management.
To uncover these needs, you may conduct one-on-one interviews or focus groups. Gather and analyze feedback to refine your development plan. This ensures the app aligns with users’ expectations and needs.
Step 3: Select the Right RPM Technology and Devices
The third step in RPM systems: select the right tech stack. Choose a savvy software partner. They’ll examine your specs and suggest fitting technologies, weigh scalability, security, and performance.
This partner will also estimate project timelines and break the work into milestones. This will keep your planning sharp and your delivery on track.
Next, pick the right devices for your health monitoring system. Look at wearables, sensors, and medical gear. They must be reliable, secure, and compatible with your RPM software platform. If making a new device isn’t an option, find a similar one to use temporarily.
To sift through the device options, hire healthcare consultants. They know the latest tech and can guide your choices and integration.
Step 4: Ensure Data Privacy, Security, and Compliance
RPM systems must follow HIPAA, FDA, and ISO 13485 standards. Beyond HIPAA compliance in software development, enforce other security measures. Add multi-factor authentication for extra protection. This ensures only approved users access the RPM system.
Encrypt electronic health records (EHR). This shields against unauthorized access and keeps patient data confidential. Also, train everyone on secure system use and provide resources and training materials. These help users grasp and apply security protocols.
These steps build trust among healthcare providers, patients, and stakeholders. They show a dedication to securing sensitive information.
Step 5: Design User-Friendly Interfaces and Dashboards
Design RPM interfaces for ease and clarity. They must simplify data, guide users smoothly, and enable efficient transactions without stress. Prioritize accessibility, clarity, and ease of use.
Key Requirements:
- Intuitive Navigation
Users should find information and features effortlessly. - Clear Data Visualizations
Use charts and graphs to display health data simply. - Attractive Design
Ensure the design is clean and reassuring without overwhelming. - Efficient Interactivity
Reduce steps for task completion to speed up communication and actions. - Responsiveness
Make sure the interface works on smartphones, tablets, desktops, and other devices. Include text enlargement, screen readers, and color contrast for accessibility and varied tech literacy levels.
First impressions count: 88% of users are not likely to come back to the website after the first bad experience. But to really engage, you must go beyond just looking pretty. Personalization and frictionless design are key, especially for Gen Z. 70% expect websites to know what they need, with experiences that feel tailor-made and enabling.
Businesses are taking note, and according to GoodFirms research, 80.8% are redesigning websites to combat the low conversion rates. Poor user experience has serious consequences: 88% are less likely to return after a bad experience. There has never been more of a need to get it right online and create a digital space that is easy to use and personalized for long-term success.
Step 6: Conducting Rigorous Testing and Quality Assurance
Incorporating testing from the beginning of the remote patient monitoring (RPM) development process is essential for identifying and resolving issues early on. Comprehensive testing can discover and address potential bugs, errors, and usability issues to achieve higher final product quality and avoid unnecessary rework expenses.
Testing must continue after the initial release of the RPM solution. This ensures that new features, enhancements, or changes do not introduce unforeseen issues or adversely impact the existing functionality. Regular testing also helps maintain the integrity, reliability, and performance of the RPM solution over time.
The standard tests for patient monitoring systems include manual, automation, and functional testing.
Factors to Consider When Selecting RPM technology and devices
Selecting the right RPM technology and devices is key to maximizing their benefits. Consider factors like accuracy, reliability, ease of use, and how well they fit into your existing systems. This ensures that the technology meets your needs and improves patient care effectively. Let’s explore each of the factors in details.
Wireless Connectivity
Wi-Fi, BLE, or infrared are needed to effectively implement remote disease monitoring. Wi-Fi provides faster data transfer and greater coverage, making it suitable for devices that require constant connectivity and large data uploads. BLE is ideal for low power, intermittent data communication, providing long battery life for wearable devices while maintaining reliable connectivity. Infrared can be used for secure data exchange over long distances.
Data Security and Device Management Solution
Ensuring the privacy and security of patient data is paramount. Personal data should be protected through layered security, which includes end-to-end encryption, secure data storage protocols, and regular security audits. Further, you can also add biometric authentication through fingerprint or facial recognition to ensure sensitive data is accessed only by authorized personnel.
Data Collection and Analytics
Determining the required data for remote patient care, establishing data transmission frequency, and ensuring adequate data storage capacity is vital. The ability to filter and analyze data accurately enables better patient care and identification of anomalies. Advanced analytics tools can also provide predictive insights. This way, healthcare providers can proactively manage patient conditions and tailor treatments more effectively.
Standards, Platforms, and Ecosystems
Ensuring interoperability and future-proofing of RPM solutions can be achieved through adherence to existing and emerging standards such as HL7, FHIR, and DICOM. Therefore, RPM system can share information without any disruptions with medical devices, electronic health records (EHRs) and other healthcare systems by aligning themselves with these standards. Building a platform that integrates various technologies and extends beyond patient monitoring creates a scalable and helpful ecosystem for remote patient monitoring.
What are the Challenges Involved in Developing an RPM System?
The development of remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems is complex. First, data integration from diverse data sources. RPM systems pull data from many devices: glucose monitors, heart rate sensors, and wearables and similar. They have all different data formats, and should be transmitted on time. This requires a good internet connection. According to HIMSS, 40% of healthcare groups struggle with data integration.
Next, data security is a major concern. RPM systems handle sensitive health data. And cyberattacks are a growing threat. In 2023, the OCR received reports of 725 data breaches, which led to the exposure or unauthorized disclosure of more than 133 million records. (HIPAA Journal)
Patient engagement also poses a challenge. Many patients don’t use RPM technologies consistently. The Journal of Medical Internet Research reports that only 30% of patients adhere to RPM. And the reason? This is due to interface issues and lack of motivation.
Lastly, regulatory requirements are complex and expensive if implemented wrong. RPM systems must comply with laws like HIPAA. Regulations change frequently, adding to the difficulty. The NHS survey in 2024 shows that 50% of developers find compliance challenging.
In summary, the design of a remote patient monitoring system involves many challenges. Developers must tackle technical, regulatory, and user-related hurdles. Overcoming these barriers will unlock the true potential of RPM systems that will benefit both, patients health and business revenue.
Empeek for Custom Monitoring Software Development
At Empeek, we specialize in creating high-performance healthcare software. With almost 20 years of experience, our services encompass custom telehealth software development, integration with EHR systems, implementation of RPM technologies, medical IoT, and many more.
End-to-End Development of Remote Cardiac Monitoring System with Wireless Heart Monitoring Device
As an RPM software development company, we have quite a few successful cases of RPM system development. For example, we developed an End-to-End Remote Cardiac Monitoring System with a Wireless Heart Monitoring Device. This system integrates a compact ECG patch with a mobile app to monitor and transmit real-time cardiac data from thousands of patients. The solution includes a cloud-based architecture for data management, a user-friendly web portal for healthcare professionals, and an Android app for seamless data transfer and patient interaction. Currently, the project delivers real-time monitoring and scalable data processing. However, there are plans to enhance it with neural network capabilities for improved accuracy.
Real-Time Health Monitoring System Using IoT
Empeek developed a cutting-edge remote patient monitoring (RPM) system in collaboration with BioBeat. Over eight months, Empeek engineered a user-friendly mobile app that integrates custom-designed wristwatches equipped with photoplethysmography (PPG) sensors. These devices capture and transmit vital signs in real-time to a secure cloud-based server, ensuring uninterrupted data flow and 24/7 remote monitoring. The scalable system not only meets stringent HIPAA and GDPR standards but also received FDA clearance and CE mark approval. It significantly reduces operational costs and enables early detection of potential health issues for timely medical interventions.

Conclusion
The future of healthcare pulses with technology. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) sparks a revolution in care. It’s more than algorithms; it’s about responsive care. RPM slashes costs and wards off serious illness.
To build RPM software, several factors collide:
- Integrate technology smoothly.
- Balance the budget carefully.
- Encourage staff to embrace change.
- Secure and accurate data is a must.
- Sync with EMR systems.
Our expertise is your asset. We craft CRM systems, IoT products, EHR/EMR systems, and medication apps. Let us bring your RPM vision to life. We’re here to help.