Today, no one would be surprised by a smartwatch that tracks heart rate or a pulse oximeter. Over the last decades, RPM has become a part of our everyday lives and a must-have for remote patient treatment. The global RPM market will reach $207.5 billion by 2028, reflecting not just a rapid spread of innovations in healthcare but also a massive shift in how medical facilities provide care. Providers and patients test remote monitoring devices as a substitute for in-hospital care, and the benefits, like cost-efficiency and convenience, make it highly attractive.
However, despite its advantages, RPM adoption is complex and requires careful consideration during implementation. You must think about potential integrations, consider data security and privacy, train staff, and manage regular system audits, among many other things we will talk about in our blog article.
Learn remote patient monitoring best practices in our blog post to adopt RPM in your organization without barriers and maximize its benefits.
Why Remote Patient Monitoring is Important
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is significant due to its numerous benefits in improving healthcare delivery and outcomes. Such devices allow doctors and nurses to monitor patients’ vital signs and conditions in real-time. It helps them determine the risk of health issues early and make the necessary interventions. On the other hand, RPM makes patients feel responsible for their health and gives them more control over the treatment process.
Read in detail about these and other key benefits that RPM provides below.
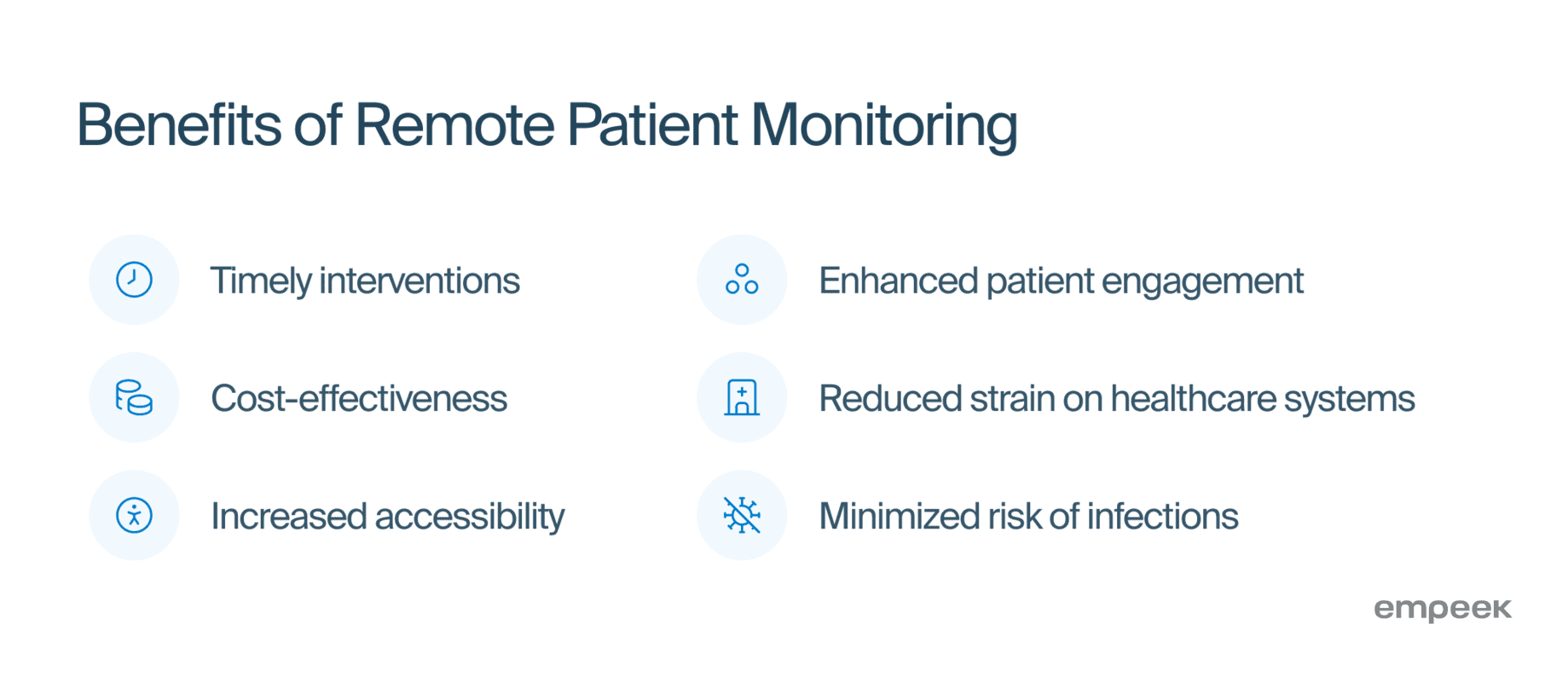
Improved Patient Outcomes Due to Timely Interventions
Correct use of remote patient monitoring enables timely interventions and personalized treatment plans, improving patient health outcomes. A systematic review published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research in 2022 showed a 29% reduction in all-cause mortality for patients with chronic heart conditions using RPM interventions.
Cost-Effectiveness
It reduces healthcare costs by enabling early detection of potential issues, which helps prevent costly emergency interventions. By continuously monitoring patients remotely, RPM allows for timely adjustments in treatment, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits and admissions. In collaboration with Philips, Banner Health conducted a telehealth pilot program focusing on remote home monitoring for patients with more than five chronic conditions. The results show a 27% decrease in the cost of care and a 32% drop in acute and long-term care expenses.
Increased Accessibility
RPM makes healthcare accessible to those in remote or underserved areas, bridging the gap between patients and providers. Telehealth services like RPM can bring healthcare to over 42 million Americans who still lack access to broadband internet.
Enhanced Patient Engagement
ItRPM empowers patients to actively manage their health by giving them real-time insight into their health data. A study conducted by Mass General Brigham and published in the Journal of the American Heart Association showed a significant decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings in patients who participated in an RPM program for hypertension management.
Reduced Strain on Healthcare Systems
RPM helps healthcare providers effectively manage chronic conditions and prevent hospital readmissions. It has been shown to reduce admissions by 33% and bed days of care by 53%. It eases the strain on healthcare facilities and allows doctors to focus on people who need urgent help.
Safety During Pandemics
In situations like the COVID-19 pandemic, RPM provides a safer alternative for healthcare delivery without the risk of infection. А study that evaluated the use of RPM during the pandemic revealed that 85.7% of participants agreed that the platform was useful and was a good response to their needs or their patients’ needs. In addition, 64.3% of them suggested that the use of these platforms should continue after the health crisis.
RPM is a new approach to healthcare that enhances patient outcomes, reduces costs, and makes quality medical services available remotely. By integrating RPM into regular care, providers can better manage chronic conditions and engage with patients more effectively. People don’t have to travel to another city to report their symptoms or have a check. A small device monitors their health remotely.
Considerations for Remote Patient Monitoring Implementation
Healthcare providers that want to allow their patients to get health monitoring and treatment remotely must implement the system step by step and follow some remote patient monitoring best practices and considerations.
When introducing RPM, several factors are critical to ensure the program’s effectiveness, regulatory compliance, and benefits for patients, doctors, and healthcare organizations. Let’s discuss these considerations below.
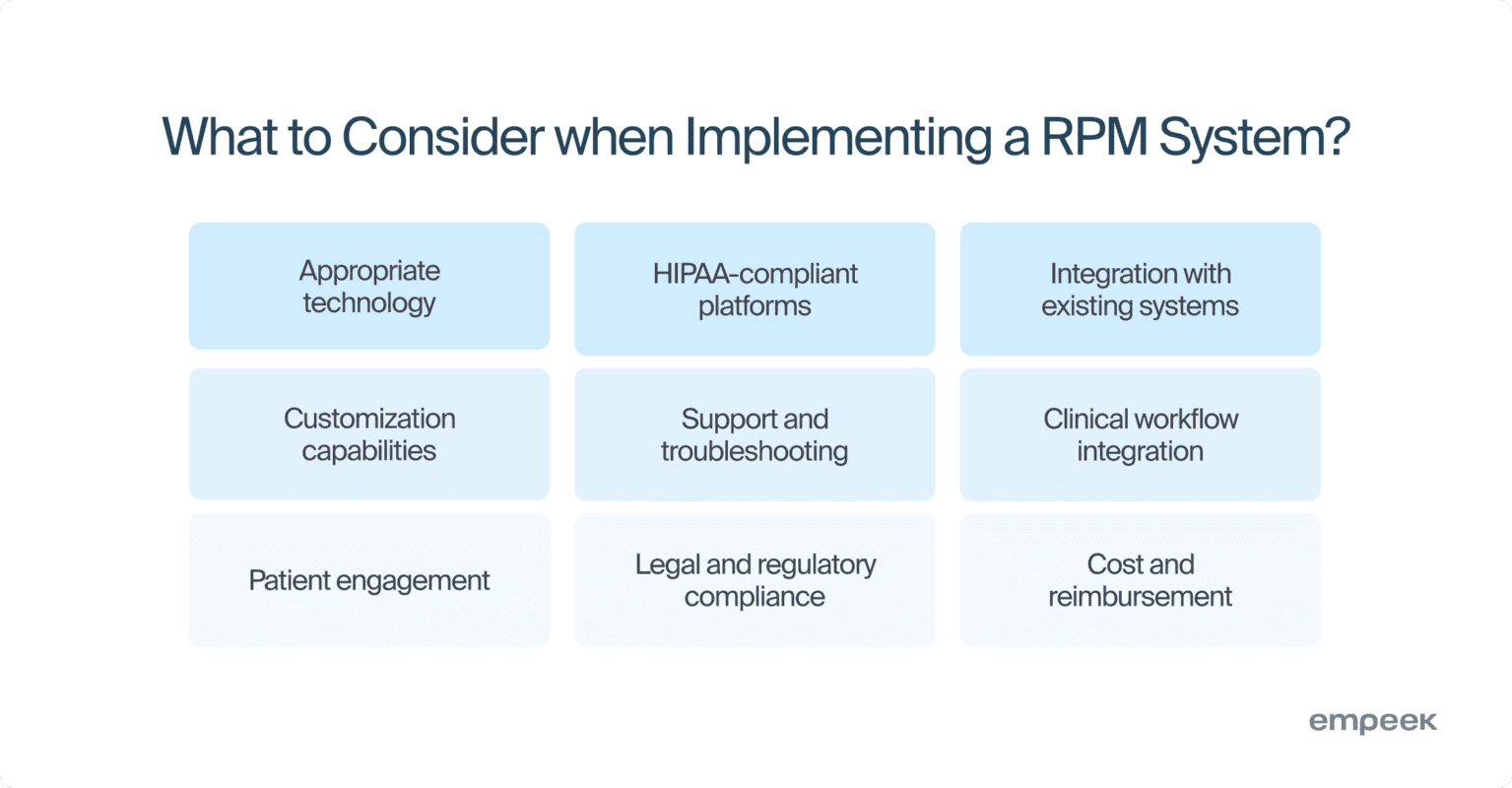
- Selection of Appropriate Technology: The choice of technology is one of the paramount considerations in remote patient monitoring. You should opt for reliable devices and software that can accurately monitor and transmit health data. Moreover, the chosen technology must be user-friendly to encourage patient adoption.
- Secure and HIPAA-Compliant Platforms: The platform utilized for RPM must adhere to HIPAA to guarantee the security and confidentiality of patient data. It must encrypt data during transmission and storage, and ensure that only authorized personnel can access patient information.
- Integration with Existing Systems: The RPM system must seamlessly integrate with current medical systems, such as Electronic Health Records (EHRs), billing systems, Laboratory Information Systems (LIS), and Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS). This ensures streamlined remote patient monitoring workflows within a healthcare facility and prevents data silos.
- Customization and Personalization: Since healthcare needs differ from patient to patient, the RPM system must be customizable to align with specific requirements. For example, you may want to configure personalized thresholds and alerts based on individual health conditions, etc.
- Support and Troubleshooting: You must have a support system to assist patients and healthcare providers with issues they encounter while using RPM software and devices. Prompt troubleshooting is a guarantee of the continuity and reliability of patient monitoring.
- Clinical Workflow Integration: When implementing RPM, it’s crucial to consider the existing clinical workflow. Healthcare professionals must follow straightforward protocols on how to respond to data received from RPM devices and what to do in case of abnormal readings.
- Patient Engagement Strategies: Maintaining patient engagement is key to long-term RPM success. Some strategies can involve regular feedback, tips with encouragement, and explanations of how RPM contributes to their overall health and well-being.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Besides HIPAA, the RPM program must follow all relevant federal, state, and local regulations governing telehealth and patient data management. Compliance with international standards, such as ISO 13485 for quality management systems in medical devices and ISO/IEC 27001 for information security management is also critical.
- Cost and Reimbursement: Comprehending the costs associated with RPM program implementation and maintenance is a critical aspect of virtual care. Additionally, exploring reimbursement options available through insurance and government programs is vital for ensuring financial sustainability.
Remote patient monitoring system implementation can be challenging if you have never done it before. The adoption process involves many nuances and pitfalls you may miss. We hope these considerations will guide you on the most critical aspects and help prepare you for RPM implementation. However, it’s always better to engage a professional RPM engineering company that can assist you with software development and integration.
Your next read: How Remote Monitoring Software Disrupts the Healthcare Sector
Remote Patient Monitoring Best Practices
To maximize the benefits of a patient health monitoring system, you should follow remote patient monitoring best practices that guarantee data accuracy, security, patient engagement, and seamless RPM integration into healthcare workflows. Here are the tried and tested remote patient monitoring tips to consider.

| Establish Clear Goals and Objectives |
| Knowing your expectations is essential for a streamlined, focused, and purpose-driven remote patient monitoring workflow. Clear goals are important for creating care plans that focus on specific results, like lowering hospital readmissions. They help use resources wisely and set standards for tracking progress. To set good goals, talk to key people like healthcare providers, administrators, and patients to understand their needs and challenges. Common goals for RPM include improved patient health, reduced emergency visits, and cost optimization. You can track KPIs such as patient satisfaction, the number of hospital visits prevented, and how well patients follow their care plans. Ensure that these goals align with the broader objectives of the healthcare organization, and apply the SMART criteria for goal setting. Once established, effectively communicate the goals among all stakeholders and institute regular reviews to ensure they stay aligned with evolving healthcare standards. |
| Train Healthcare Professionals and Staff |
| Training healthcare staff is one of the core remote patient monitoring best practices. The effectiveness of an RPM program heavily depends on the competence of those who operate, manage, and respond to it. Standard training encompasses technical proficiency, data interpretation, patient communication, and response protocols. Healthcare professionals must know how to operate devices and read data, communicate effectively with patients, and understand appropriate response measures. Since healthcare is an ever-evolving field, training must be dynamic and ongoing. Regular updates and refresher courses are necessary to keep up with technological advancements and emerging healthcare trends. |
| Gather Meaningful Patient Data |
| Collecting accurate patient data with all the specifics of their conditions is essential for successful diagnostics and treatment. Calibrating devices, validating data, and adequately training patients to use monitoring tools can help you achieve this. You must also analyze patient data using predictive modeling, AI, and machine learning to identify patterns and get informative insights. |
| Consider RPM Reimbursement Options |
| You need to understand the specific RPM billing and reimbursement policies, as they can vary. Key practices include using the correct billing codes, such as CPT 99453 for setup and CPT 99457 for ongoing monitoring, to ensure claims are processed correctly. Proper documentation of patient interactions and monitoring activities is crucial for meeting reimbursement requirements. Stay updated with regulatory changes to maintain compliance and ensure financial sustainability for RPM services. |
| Incorporate Patient Feedback and Address the Concerns |
| By actively gathering feedback, healthcare providers gain insights into user experiences, RPM effectiveness, and areas for improvement. This ensures that the RPM program remains aligned with patients’ needs and preferences. To seamlessly integrate patient feedback and address concerns, you must establish channels for easy feedback submission and consistently analyze the gathered information for actionable insights. |
| Motivate Patients to Follow the Rules Through Feedback |
| Provide real-time feedback to patients through mobile apps or monitoring devices, showing how their actions (e.g., taking medication or following a prescribed diet) impact their health. A valuable strategy is using gamification such as badges, points, or progress bars to motivate patients to stay consistent with their monitoring routines. Equally important is establishing regular check-ins between healthcare providers and patients to review the data and reinforce the value of ongoing monitoring. |
RPM Barriers and Mistakes Made in RPM Programs
In the quest to optimize healthcare delivery through RPM, it’s essential to acknowledge and address the issues that may arise during its implementation. Mistakes made in RPM programs range from technical issues like unreliable connectivity and device malfunctions to human factors such as low patient engagement or inadequate staff training. By knowing these traps beforehand, you can make informed decisions to prevent costly mistakes.
Technological Challenges
Many clients encounter compatibility, scalability, and data management difficulties when integrating RPM technology into their existing systems. These challenges can arise from outdated infrastructure, lack of standardization, or the inability of RPM platforms to communicate with existing systems. As the volume of patient data grows, managing and securely storing this information can become increasingly complex without the right tools and strategies in place.
| Solution: Invest in custom solutions that are compatible with your existing systems and offer scalable options that can adapt as your needs evolve. |
Patient Adoption and Engagement
Convincing patients to use RPM devices and ensuring continued engagement is often a stumbling block. Patients may be resistant to change or find the technology intimidating. In fact, in the US, about 25% of older adults (65+) do not have the Internet, and approximately 40% do not use a smartphone.
| Solution: Develop effective patient onboarding strategies to provide ongoing support, eliminate any concerns, and enhance engagement. |
Staff Training and Adaptation
Healthcare staff may be unfamiliar or uncomfortable with the new technology, necessitating comprehensive training programs which can be time-consuming and costly.
| Solution: Encourage your staff to participate in the RPM adoption process when possible, ask for feedback and share updates. It will keep them engaged and help learn how to use the new tools faster. |
Financial Constraints
The initial investment required for RPM systems can be substantial. Clients often struggle with budget constraints and figuring out the return on investment.
| Solution: Seek outside help and consult with professionals in the RPM field. Also, investing more finances and time into the Discovery Phase may drastically change the cost. Proper discovery helps to focus on the necessary features and understand the ROI beforehand. |
Data Security and Compliance
Ensuring that RPM systems are secure and comply with regulations like HIPAA is a significant concern, as the protection of patient data is paramount.
| Solution: Each RPM system must be designed with robust security measures, such as end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure data storage, to comply with HIPAA regulations and protect patient information from breaches. You must also organize regular security audits and carefully manage data access. |
Connectivity Issues
In some cases, unreliable internet connection can hinder the consistent transmission of data, particularly in rural areas where network coverage may be sparse.
| Solution: Use RPM devices that support multiple data transmission methods, such as cellular networks, satellite, or offline data storage that syncs when a connection becomes available. |
Considering these RPM barriers and issues beforehand will help you plan smoother implementation and achieve a better outcome for patients and medical staff. A well-planned RPM strategy with custom solutions can improve care and optimize healthcare delivery.
RPM Examples and Case Studies by Empeek
Now let’s turn the attention to real-world examples that showcase the effectiveness of RPM in improving patient outcomes. Check out how Empeek has implemented RPM across various healthcare settings for valuable insights.
Real-Time Health Monitoring System Using IoT
Empeek has developed a real-time wireless medical monitoring system that captures, analyzes, and decodes patients’ vital signs. This IoT-based solution facilitates communication between healthcare providers and patients with real-time data synchronization. The system has improved patient monitoring and offered health-conscious individuals and healthcare facilities a convenient platform for continuous health data collection. Read the full case study.
Remote Patient Monitoring Software that Serves Over 10k Users
We have created an RPM portal that uses cellular and Wi-Fi technology to monitor patients in real-time. It gathers data from wearable devices to allow healthcare providers to track vital signs remotely for assessment and recommendations and take instant measures in case of abnormalities. Read the full case study.
Learn more about our RPM development services and contact us for medical engineering consulting and help.
Conclusion
Now you know the core considerations and best practices to mind when implementing RPM in telehealth care. Be sure to integrate a user-friendly, secure, and customizable platform to improve the quality of medical services and make them truly accessible.
However, the implementation of RPM systems is not without its challenges. From technological integration to patient engagement, staff training, financial considerations, data security, and connectivity, the barriers can be multifaceted. That’s why, for successful implementation of RPM, healthcare organizations should collaborate with a reliable technology partner. With our expertise in remote patient monitoring development, we can assist in the seamless integration of remote monitoring technology into existing telehealth services.
Contact Empeek to get an experienced healthcare software development partner who can build a custom RPM solution or help implement an off-the-shelf system.